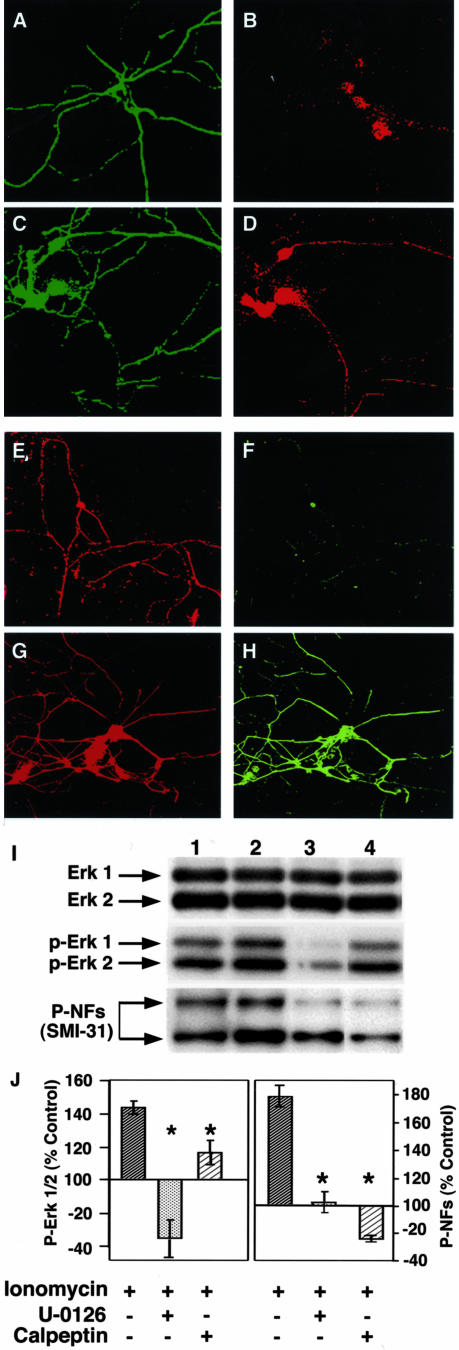
Figure 4.
The Mek1,2 inhibitor, U-0126, and calpeptin attenuate ionomycin-induced Erk1,2 activation and NF-phosphorylation in cerebellar granule neurons. A–D: CG neurons (7 DIV) either vehicle-treated (A, B, E, F) or treated with 0.5 μmol/L ionomycin (C, D, G, H), were immunostained with antibodies against β-tubulin (A and C), p-Erk1,2 (B and D), NF-L (E and G), and phospho-NF-M (F and H). E: The CG neurons (7 DIV), either vehicle-treated (lane 1) or treated with ionomycin (0.5 μmol/L; lane 2) or ionomycin together with either U-0126 (10 μmol/L; lane 3) or calpeptin (20 μmol/L; lane 4) for 24 hours, were subjected to SDS-PAGE (equal protein loading, 15 μg) and Western blot analysis with either anti-Erk1,2, anti p-Erk1,2, or SMI 31 against phospho-NF-H and neurofilament M. F: Bar graph shows the relative band intensities of p-Erk1,2 (left) and phospho-NF-M (right). The values are the mean ± SEM of three to five separate experiments. *, P < 0.05.