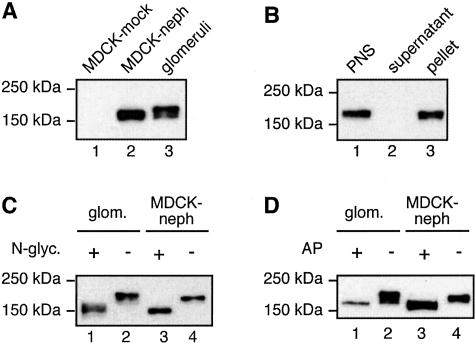
Figure 1.
Immunoblot analysis of nephrin expressed in MDCK cells. A: In MDCK cells stably expressing nephrin (lane 2), nephrin appears as an ∼180-kd band that migrates slightly faster than endogenous nephrin in glomerular lysates (lane 3). Nephrin is not detected in MDCK cells infected with vector alone (lane 1). MDCK cells were retrovirally infected with a vector carrying nephrin and selected with G418 to obtain cells stably expressing nephrin. MDCK-nephrin cell and glomerular lysates were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and 10 μg of the lysates were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-nephrin 043 IgG. B: Nephrin is detected in membrane fractions when expressed in MDCK cells. MDCK-nephrin cells were lysed with hypotonic buffer followed by fractionation of the postnuclear supernatant (PNS, lane 1) into cytosolic (supernatant, lane 2) and membrane (pellet, lane 3) fractions. Equal volumes of the fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting as in A. C: Nephrin is N-glycosylated when expressed in MDCK cells. N-glycanase induces a shift in the mobility of nephrin in both glomeruli (lanes 1 and 2) and MDCK-nephrin cells (lanes 3 and 4). Ten μg of MDCK-nephrin cell and glomerular lysates were incubated with 2.5 mU of N-glycanase at 37°C for 4 hours and immunoblotted as in A. D: Nephrin is phosphorylated when expressed in MDCK cells. Alkaline phosphatase induces a shift in the mobility of nephrin in both glomeruli (lanes 1 and 2) and MDCK-nephrin cells (lanes 3 and 4). Ten μg of MDCK-nephrin cell and glomerular lysates were incubated with 18 U of alkaline phosphatase at 30°C for 8 hours and immunoblotted as above.