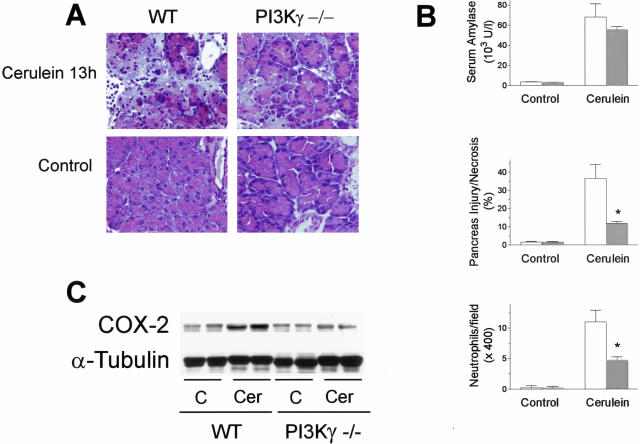
Figure 3.
Effects of PI3Kγ deletion on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Mice were administered 13 intraperitoneal injections of cerulein and killed 1 hour after the last injection of cerulein. A: Representative micrographs of morphological alterations induced in exocrine pancreas by 13 hours of cerulein administration (cerulein 13h) compared with 13 hours of saline administration (Control), in wild-type (WT) and PI3Kγ-deficient (PI3Kγ−/−) mice. Thirteen hours of cerulein administration induced evident morphological alterations and massive neutrophil infiltration of the exocrine pancreas compared with controls. Foci of coagulative necrosis are also evident. Original magnifications, ×400. B: Quantitation of cerulein-induced pancreatic injury. Serum amylase activity, acinar cell injury/necrosis, and neutrophil infiltration were measured as described in the text. Wild-type mice, open columns; PI3Kγ-deficient mice, shaded columns. Results are mean ± SEM values for five or more animals in each group. *, P < 0.05 versus control. C: Effects of PI3Kγ deletion on pancreatic COX-2 expression during cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Pancreata from wild-type (WT) and PI3Kγ-deficient (PI3Kγ−/−) mice were harvested after 13 hours from the beginning of saline (C) or cerulein (Cer) administration, and analyzed by Western blot for COX-2 and α-tubulin expression, as described in Materials and Methods.