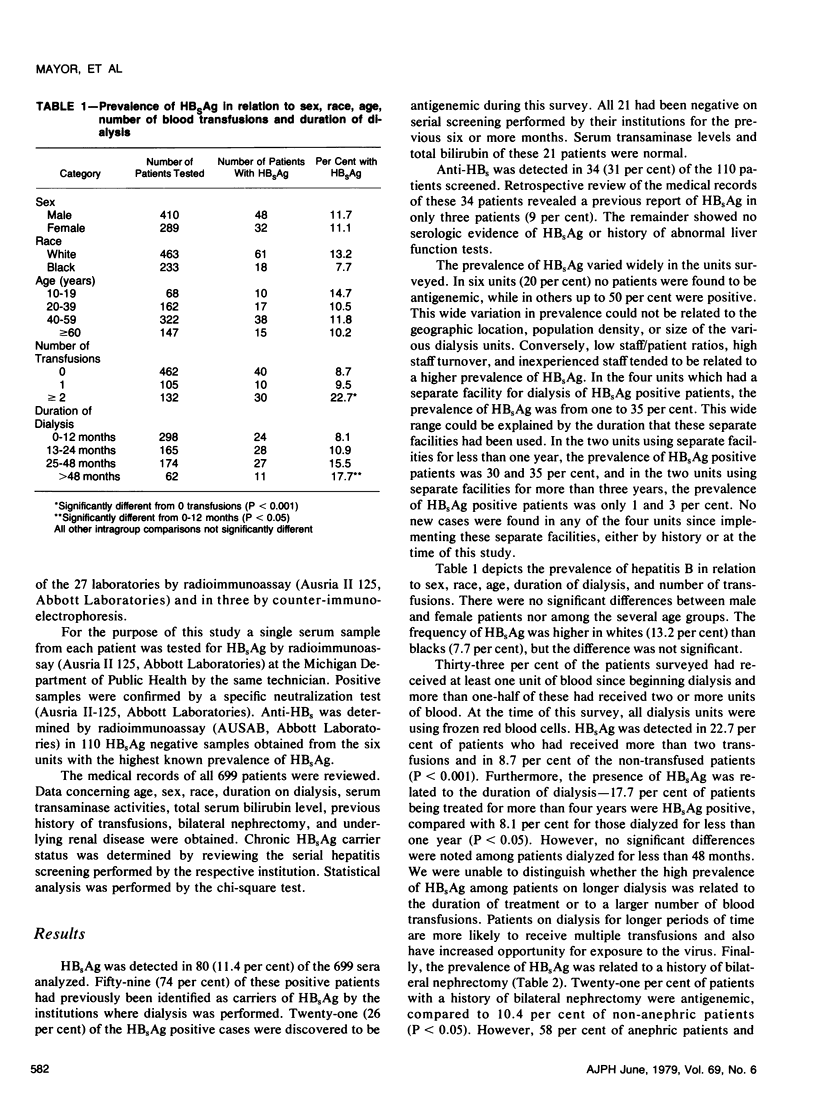
Abstract
A large epidemiological survey of inhospital chronic hemodialysis patients was conducted in 27 (93%) of the 29 dialysis centers in Michigan. Serum was collected from 699 patients on chronic maintenance hemodialysis for periods from one month to eight years. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was determined in all patients by radioimmunoassay and positive samples were confirmed by specific neutralization. Antibody against HBsAg (anti-HBs) was determined by radioimmunoassay in 110 HBsAg negative patients from six dialysis units with a high prevalence of hepatitis B. HBsAg was detected in 80 (11.4%) patients distributed among 21 (78%) of 27 dialysis units and anti-HBs in 34 (31%) patients from the selected dialysis units. The prevalence of HBsAg was related to duration of dialysis, number of blood transfusions, and to a history of bilateral nephrectomy, but not to age, sex, race, nor the underlying renal disease. Twenty-one (26%) of the 80 HBsAg positive patients had not been previously identified by the clinical laboratories of their institutions. Since preventive measures were not taken in the care of these inapparent carriers of HBsAg, they represent an unrecognized risk.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Seeff L. B., Kaplan P. M., McAuliffe V. J., Wright E. C., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Zimmerman H. J. Type B hepatitis: the infectivity of blood positive for e antigen and DNA polymerase after accidental needlestick exposure. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 21;295(17):909–913. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610212951701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Tabor E., Meryman H. T., Hoofnagle J. H., Kahn R. A., Holland P. V., Gerety R. J., Barker L. F. Transmission of hepatitis V virus infection by transfusion of frozen-deglycerolized red blood cells. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):637–642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darani M., Gerber M. Letter: Hepatitis-B antigen in vaginal secretions. Lancet. 1974 Oct 26;2(7887):1008–1008. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood J. B., Curtis J. R., Wing A. J., de Wardener H. E. Hepatitis in a maintenance hemodialysis unit. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jul;69(1):59–66. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi R. A., Forrest J. N., Bryan J. A., Hanson B. F., Dismukes W. E. Hemodialysis-associated hepatitis. JAMA. 1973 Jul 23;225(4):384–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J., Cameron C. H., Dane D. S. Hepatitis-B antigen in saliva and semen. Lancet. 1974 Jan 19;1(7847):71–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani M. R., Mayor G. H., Greenbaum D. S., Hugget D. O., Patterson M. J. Hepatitis B surface antigen in urine of hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1978 Apr;13(4):324–328. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London W. T., Di Figlia M., Sutnick A., Blumberg B. S. An epidemic of hepatitis in a chronic-hemodialysis unit. Australia antigen and differences in host response. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 11;281(11):571–578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909112811101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Lindholm A., Lundin P., Iwarson S. A new antigen-antibody system. Clinical significance in long-term carriers of hepatitis B surface antigen. JAMA. 1975 Jan 27;231(4):356–359. doi: 10.1001/jama.231.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzur S. Menstrual blood as a vehicle of Australia-antigen transmission. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):749–751. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison C. P., Maynard J. E., Berquist K. R., Webster H. M. Serological and epidemiological studies of hepatitis B in haemodialysis units. Lancet. 1973 Jul;2(7822):172–174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Bryan J. A., Hanson B. Hemodialysis-associated hepatitis in the United States--1972. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):109–113. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W., Prince A. M., Grady G. F., Mann M. K., Levine R. W., Friedman E. A., Jacobs M. J., Josephson A., Ribot S., Shapiro F. L. Hepatitis B infection. A point-prevalence study in 15 US hemodialysis centers. JAMA. 1974 Feb 25;227(8):901–906. doi: 10.1001/jama.227.8.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W. Recent advances in the study of the epidemiology of hepatitis B. Am J Pathol. 1975 Dec;81(3):629–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarejos V. M., Visoná K. A., Gutiérrez A., Rodríguez A. Role of saliva, urine and feces in the transmission of type B hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Dec 26;291(26):1375–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197412262912602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


