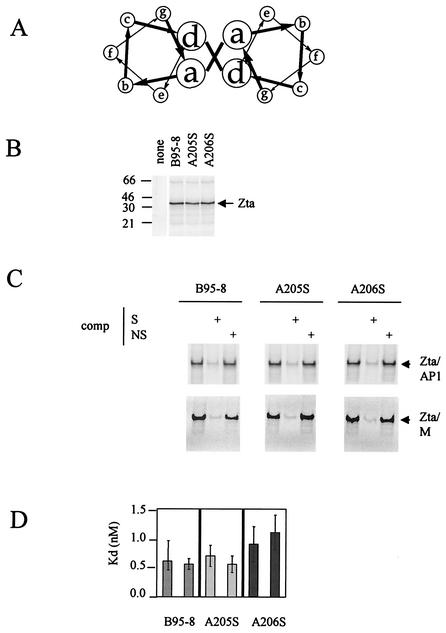
FIG. 2.
All three natural variants within the dimerization domain of Zta interact equivalently with DNA. The locations of amino acid residues A205 and A206 occur at b and c positions of the heptad repeat in the predicted structure of the coiled coil as shown in panel A. The coding sequences for A205 and A206 were each altered by using site-directed mutagenesis to encode serine within the B95-8 Zta cDNA (27). The resulting plasmids, B95-8, A205S, and A206S, were transcribed and translated in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate system as for Fig. 1. The proteins were fractionated on a sodium dodecyl sulfate-15% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel (B). The input plasmid is indicated above each lane, and the migration of molecular weight markers is given on the left (in kilodaltons). Following exposure to a phosphorimager (Storm), the concentrations of the proteins were normalized and their ability to interact with a double-strand version of a canonical AP1 site and a ZRE from the BSLF2+BMLF1 promoter (M) was evaluated by EMSA at 20°C (C). The input proteins are indicated above with the radiolabeled probe (2 ng), and nonlabeled competitor (comp) DNA—either specific, S, (AP1) (500 ng), or nonspecific, N, (500 ng)—is shown above each track. (D) The Kd values of the interaction of the B95-8, A205S, and A206S Ztas were determined by EMSA with increasing probe concentration. The data were quantitated by using phosphorimaging, and the concentrations of bound and free probe were determined according to the method described by Stone et al. (33).