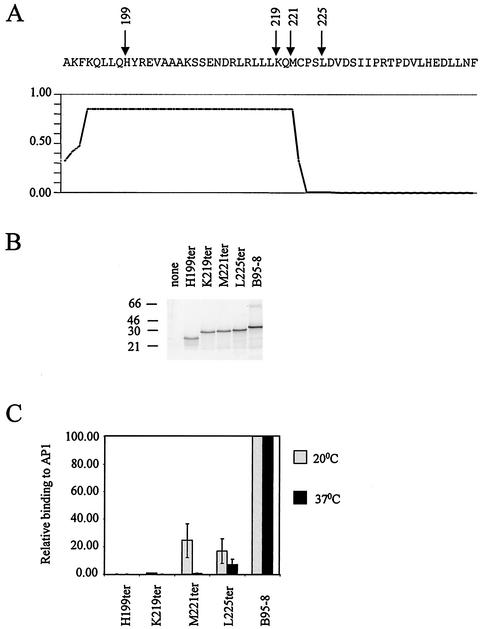
FIG. 5.
The relevance of the C-terminal region of Zta for DNA binding was investigated. A series of truncations of the Zta coding sequence were generated (based on the B95-8 sequence) by using site-directed mutagenesis. The positions where the ter codons were introduced are indicated on the sequence (residues 191 to 245) in panel A. The prediction of the extent of coiled coil formation through this region is indicated graphically below. The x axis is aligned with the amino acid sequence above, and the y axis represents the predictive value of forming a coiled coil (17). The ter mutant series, together with B95-8 sequence, were transcribed and translated in vitro as described in the Fig. 1 legend. The resulting proteins were fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-15% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and were analyzed by phosphorimaging (Storm) (B). The migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left in kilodaltons. Following normalization for protein concentration (taking into account the number of methionine residues in each protein), their ability to specifically interact with a ZRE (AP1) was assessed by using EMSA at both 20 and 37°C. Following phosphorimaging, the amount of DNA-binding activity relative to B95-8 was determined (C). Error bars represent the standard deviations derived from duplicate experiments.