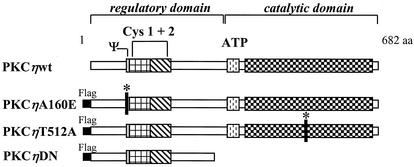
FIG. 4.
Construction of PKCη mutants. PKCη is a member of the novel PKC family consisting of 682 aa. Besides the catalytic domain comprising the substrate recognition and ATP-binding sites, PKCs contain a large regulatory domain. This domain is characterized by the presence of a pseudosubstrate sequence (Ψ) and two cysteine-rich Zn finger motifs (Cys 1 + 2) binding the cofactors phosphatidylserine, DAG, and TPA. PKCηA160E is a constitutively active mutant form of human PKCη in which the pseudosubstrate region was altered to prevent it from binding to the catalytic domain, keeping the enzyme in an open conformation. The inactive mutant PKCηT512A was obtained by an amino acid substitution for the PDK1 phosphorylation site T512, mimicking the nonphosphorylated residue. The dominant negative mutant PKCηDN was constructed by deleting the C terminus from aa 297 onwards and should block the substrate recognition site of endogenous PKCη through high-affinity binding. A Flag epitope was N-terminally fused to all PKCη mutants, enabling their distinction from the endogenous enzyme through immunodetection.