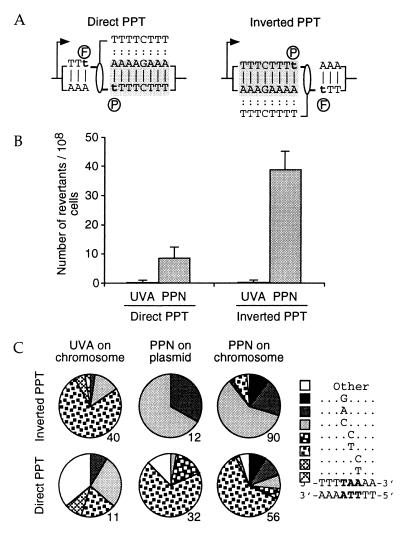
Figure 3.
The frequency and types of mutations generated by the PPN TFO depend on the orientation of the target sequence with respect to the gene promoter. (A) Sequence of the target in the direct and inverted orientations showing the preferential orientation of the psoralen crosslink positioned by the TFO. (B) Number of revertants generated at the target site in the direct and inverted orientations. CmY826-derived cells carrying a direct or inverted HIV-1 PPT were electroporated and selected as in Fig. 2. (C) Mutations generated on exogenous or endogenous targets are similar in nature. Graphs indicate the proportion of each type of mutation, determined by sequencing the mutants obtained through UVA irradiation (UVA on chromosome), through action of the PPN TFO on endogenous HIV-1 PPT targets (PPN on chromosome), or in experiments in which the triplex was preformed on plasmids (YEplac112_ura3∷hiv1pur and _ura3∷hiv1pyr) in vitro (PPN on plasmid). The number of mutants analyzed is indicated below each graph. A similar effect of the orientation of the target was observed in the FF18 733 background, so that sequencing results obtained in both the CmY826 and the FF18 733 backgrounds were pooled.