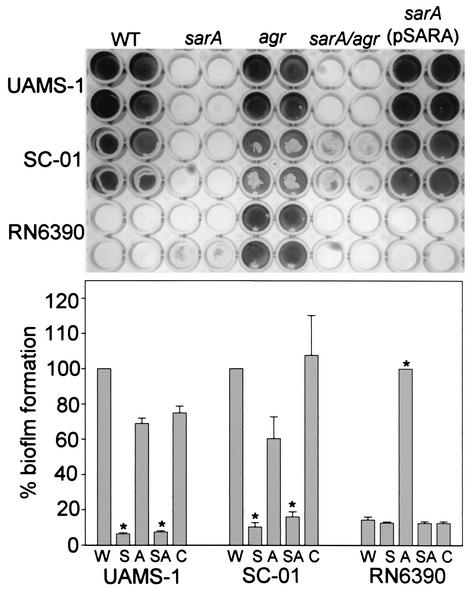
FIG. 4.
Complementation of sarA defect. Top panel: wild-type (WT) strains are identified on the left side of the figure. Specific mutations introduced into each strain are indicated at the top. All strains were grown in TSB supplemented with both glucose and sodium chloride. Biofilm assays were done using precoated plates. Complementation of the sarA mutants was done with a plasmid containing the P1 promoter and sarA ORF (3). Bottom panel: quantitative analysis of biofilm formation was done by spectrophotometric analysis. In the case of strains UAMS-1 and SC-01, results for the sarA mutant (S), the agr mutant (A), the sarA/agr double mutant (SA), and the pSARA-complemented sarA mutant (C) are shown relative to those for the wild-type strain (W). In the case of RN6390, results are shown relative to those of the agr mutant. Asterisks denote statistical significance (P < 0.05) on the basis of the analysis of five plates, with each plate containing wells that were duplicates of those shown in the upper panel. Statistical comparisons were done using Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance.