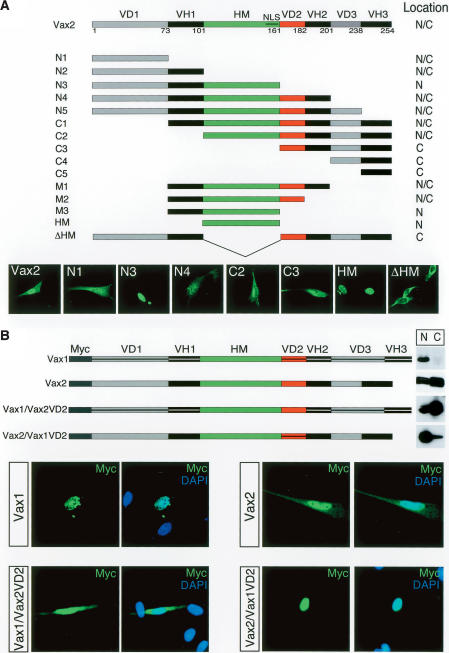
Figure 2.
Identification of the critical domain for Vax2 cytoplasmic localization.(A) Subcellular localization of Vax2 deletion mutant proteins. The diagrammed panel shows Vax2 deletion mutants (N1, N2, etc.) were fused to GFP and expressed in cultured Schwann cells. Transfected cells were then monitored for cytoplasmic (C), nuclear + cytoplasmic (N/C), or nuclear (N) localization of the indicated GFP fusion proteins. Selected examples of differential localization for wild-type Vax2 and for the N1, N3, N4, C2, C3, HM, and ΔHM deletion constructs are displayed in the GFP images below the construct diagrams. (VH) Vax homologous domain; (VD) Vax divergent domain; (HM) homeodomain; (NLS) nuclear localization signal in the HM. (B) VD2-dependent cytoplasmic retention of Vax2. Myc-tagged chimeric proteins of Vax1 containing the Vax2 VD2 [Vax1/Vax2(VD2)], or of Vax2 containing the Vax1 VD2 [Vax2/Vax1(VD2)], were expressed in Schwann cells, and their subcellular localization was monitored by immunostaining with a mouse anti-Myc monoclonal antibody (green), together with DAPI (nuclear) counterstaining (blue). Vax1 and Vax2/Vax1(VD2) are nuclear proteins (upper left and lower right set of immunofluorescence images, respectively), whereas Vax2 and Vax1/Vax2(VD2) are distributed between the nucleus and cytoplasm (upper right and lower left set of panels, respectively). Nuclear (N) versus cytoplasmic (C) localization was also monitored by Western blot of pellet (N) and supernatant (C) fractions of low-speed centrifugations of cell culture homogenates, as for the blots in Figure 1D.