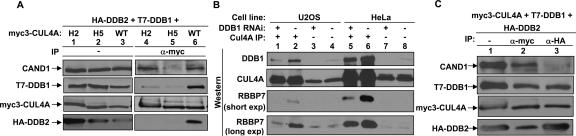
Figure 4.
DDB1 bridges WD40 repeat proteins to CUL4. (A) Intact H2 and H5 helices of CUL4A are required for binding with DDB1 and DDB2. 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing indicated proteins. The steady-state level and protein–protein interactions were determined by direct immunoblotting and IP-Western, respectively. (B) Silencing DDB1 reduced CUL4A–RBBP7 association. DDB1 was knocked down by the infection of a retrovirus expressing shRNA targeting DDB1. The steady-state level and CUL4A–RBBP7 association were determined by direct Western and IP-Western analysis. (C) CAND1 and DDB2 form mutually exclusive complexes with CUL4A. 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing HA-DDB2, T7-DDB1, and myc3-CUL4A. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated and blotted with indicated antibodies.