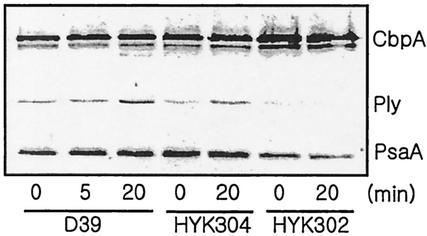
FIG. 6.
Induction of virulence-associated genes by heat shock. Exponentially growing encapsulated S. pneumoniae D39 (A600 = 0.1) and its isogenic clpP (HYK302) and clpL (HYK304) derivatives were heat shocked at 42°C for 20 min. Then 0.6 ml of culture was centrifuged, and the cell pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer, followed by boiling for 3 min. Subsequently, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with a mixture of polyclonal antisera raised against CbpA, pneumolysin, and PsaA. The relative positions of CbpA, pneumolysin (Ply), and PsaA are indicated.