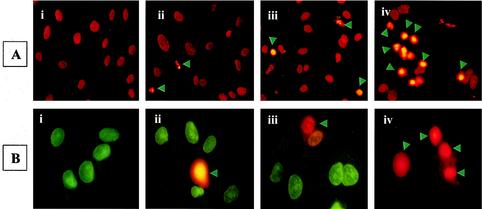
FIG. 3.
Induction of EC apoptosis during R. rickettsii infection. EC were infected for 12 h with or without concurrent inhibition of NF-κB response, followed by in situ detection of apoptosis. Panels represent (i) no treatment, (ii) incubation with MG132, (iii) infection with R. rickettsii, and (iv) infection in the presence of MG132. (A) TUNEL staining showing apoptotic nuclei with a condensed appearance (arrowheads). (B) Live-dead assay distinguishes normal and apoptotic cells. Healthy cells acquire green cell-permeating cytodye, while apoptotic cells (indicated by arrowheads) capture both the cytodye and the nonpermeating propidium iodide, resulting in orange fluorescence.