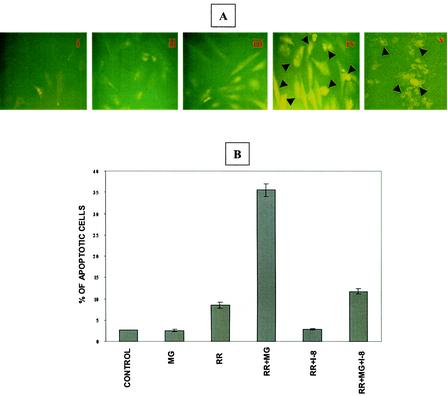
FIG. 4.
Activation of caspase-8 during R. rickettsii-induced EC apoptosis. (A) Immunofluorescent detection of caspase-8 activation. The conditions in panels i through iv are identical to those in Fig. 3. Panel v is a positive control showing activation of caspase-8 in EC exposed to etoposide (300 μM). Arrowheads point to activated caspase-8-positive cells. (B) Effect of a specific inhibitor of caspase-8, IETD-CHO, on infection-induced apoptosis. EC were treated with 10 μM IETD-CHO (I-8) in the presence or absence of MG132, followed by infection with R. rickettsii. Quantitation of apoptosis was performed by TUNEL analysis as described in the text. A total of 500 cells were enumerated for each condition. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of apoptotic cells ± SEM from three independent experiments.