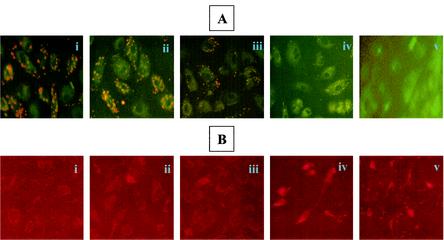
FIG. 5.
Mitochondrial alterations during R. rickettsii-induced endothelial apoptosis. (A) Mitocapture staining to determine the status of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (Δψm) during EC infection. Representative images of (i) untreated and uninfected, (ii) MG132-treated, (iii) R. rickettsii-infected, (iv) infected and MG132-treated cells, and (v) staurosporine-treated (positive control) cells. The mitocapture dye yields fluorescence and accumulates in mitochondria of healthy cells. Note the absence of dye uptake in panels iv and v, indicating disruption of Δψm. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of cytochrome c distribution under similar experimental conditions. Diffuse staining in iv and v indicates release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, whereas the punctate staining in panels i, ii, and iii indicates mitochondrial localization of cytochrome c.