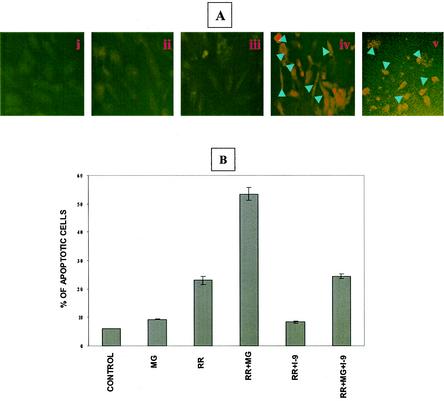
FIG. 6.
Activation of caspase-9 during R. rickettsii-induced EC apoptosis. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence-based detection of caspase-9 activation. The experimental conditions in panels i through iv are identical to those in Fig. 3. Panel v represents a positive control showing activation of caspase-9 in EC exposed to staurosporine (2 μM). Arrowheads point to cells with activated caspase-9. (B) Effect of a specific inhibitor of caspase-9, LEHD-CHO, on infection-induced apoptosis. EC were treated with 10 μM LEHD-CHO (I-9) in the presence of absence of MG132, followed by infection with R. rickettsii. Quantitation of apoptosis was performed by TUNEL analysis of at least 500 cells for each condition. Results are expressed as the mean percentage of apoptotic cells ± SEM from three independent experiments.