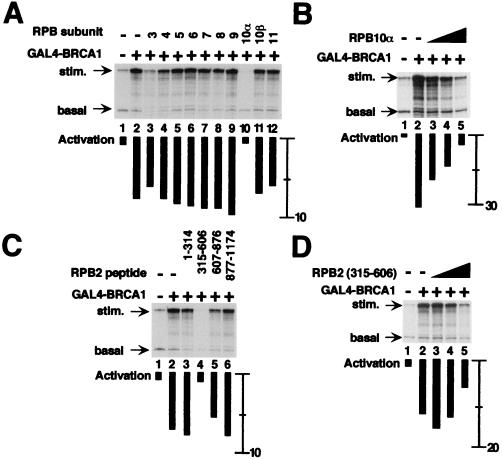
Figure 2.
Pol II subunits hRPB10α and hRPB2 mediate BRCA1-dependent transcriptional activation. All reactions contain purified basal transcription factors, the coactivator PC4, and core Pol II in the absence or presence of GAL4-BRCA1. Individual Pol II subunits fused to GST were added as indicated. Transcription from the GAL4-dependent template resulted in the accumulation of 380-nucleotide RNA (stim.), and transcription from a control template lacking GAL4 response elements resulted in accumulation of 210-nucleotide RNA (basal). The relative increase in transcription upon addition of activator, quantified by using PhosphorImager analysis, is indicated by black bars under each lane. For comparison, the activation in lane 2 of A (absence of added Pol II subunit) is eight-fold. (A) Inhibition of BRCA1-dependent stimulation of transcription by 300 ng of GST fusion of each hRPB3 to hRPB11 (lanes 3–12). (B) Titration of RPB10α results in an incremental decrease in BRCA1-stimulated transcription. GST-hRPB10α was included in reactions at 75 ng (lane 3), 150 ng (lane 4), and 300 ng (lane 5). (C) Inhibition of BRCA1-dependent transcriptional activation by hRPB2 peptides. Twelve hundred nanograms of each fragment were added as indicated. (D) Titration of hRPB2(315–606) results in an incremental decrease in BRCA1-stimulated transcription. GST-hRPB2(315–606) was included in reactions at 300 ng (lane 3), 600 ng (lane 4), and 1,200 ng (lane 5).