Figure 5.
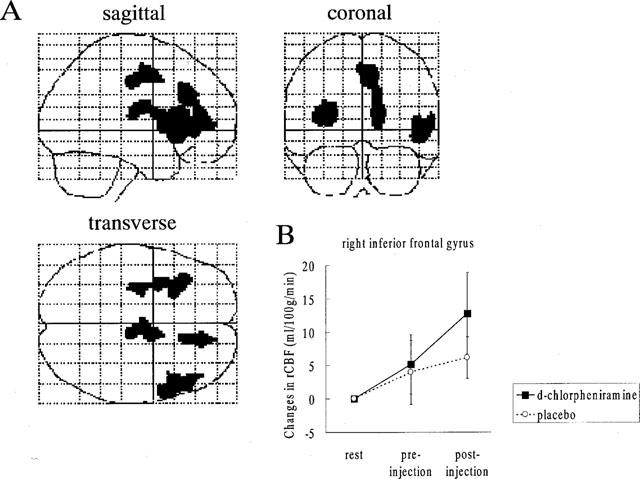
(A) Brain areas where the rCBF activation was relatively increased after the administration of 2 mg d-chlorpheniramine. The rCBF images obtained in the pre-injection scans were subtracted from those in the post-injection scans during visual discrimination task. Areas of significant relative rCBF increases (P<0.05, corrected) are shown as through-projections onto representations of standard stereotactic space. A significant increase in rCBF was observed on the right inferior frontal gyrus (45), the anterior cingulate gyrus (32, 24) and the left insula. The exact coordinates of the local maxima within the areas of activation and their Z statistics are given in Table 1. (B) Relative changes in the right inferior frontal gyrus (48 34 6) in the d-chlorpheniramine (2 mg) group and placebo group. The voxel was selected from the local maxima from the within-group analysis of the drug effect on task. The result indicated that the right inferior frontal cortex was activated only in drug-treated subjects.
