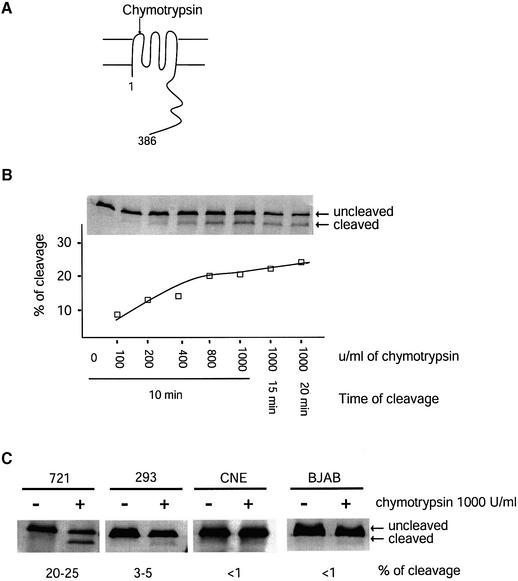
Fig. 2. The fraction of LMP1 accessible to cleavage in live cells by chymotrypsin differs among cell types. (A) The first extracellular loop of LMP1 can be cleaved by chymotrypsin when LMP1 is at the cell surface. The cleaved product can be separated from intact LMP1 by SDS–PAGE and identified by western blotting using an antibody against the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of LMP1 (Liebowitz et al., 1986). (B) Live 721 cells were treated with different concentrations of chymotrypsin for different periods of time as indicated and as described in Materials and methods. The chymotrypsin-treated cells were lysed in 1× RIPA. Cell lysates from 5 × 104 cells for each sample were separated by SDS–PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The LMP1 was detected with a polyclonal rabbit anti-LMP1 antibody followed by 35S-labeled goat anti-rabbit antibodies. The cleaved LMP1 and the uncleaved LMP1 were quantified. The percentage of cleavage was calculated as [cleaved LMP1/(cleaved LMP1 + uncleaved LMP1)] and plotted. Shown is a representative of three independent experiments. (C) Live 721 cells, and 293, CNE and BJAB cells transiently expressing LMP1 were treated with 1000 U/ml chymotrypsin for 10 min at room temperature. The fractions of LMP1 being cleaved were calculated as described in (B).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.