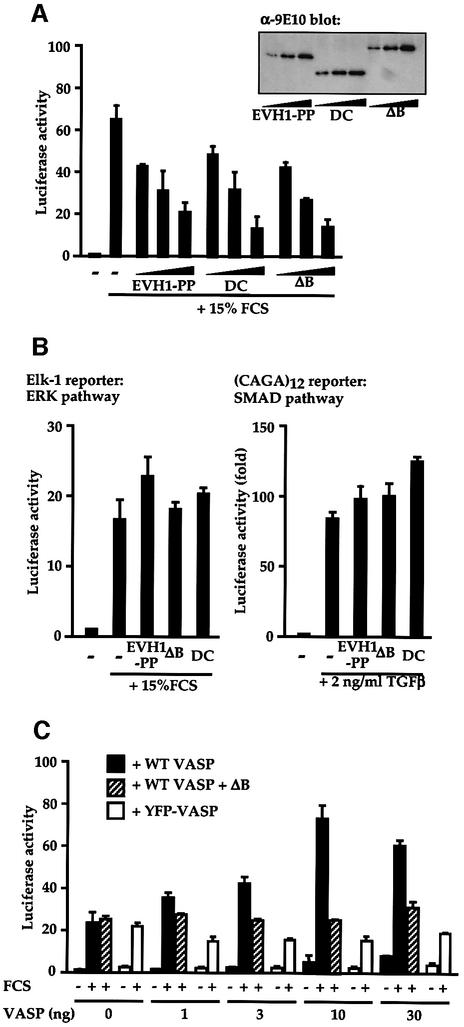
Fig. 5. Serum-induced SRF activation requires functional VASP. (A) Interference with serum-induced SRF activation. Cells transfected with the SRF reporter and plasmids expressing VASP mutants (0.1, 0.3 and 0.9 µg) were analysed for reporter activity before and after serum stimulation. Inset: VASP immunoblot. (B) Interference by the VASP mutants is signal pathway-specific. Cells transfected with NLex.ElkC and LexOP.Luc (left; ERK pathway) or CAGA12.Luc (right; SMAD pathway) together with control plasmid RLTK and expressed VASP mutants (0.9 µg). Luciferase activity was determined following stimulation with 15% FCS (left) or 2 ng/ml TGFβ (right). (C) Functional VASP is required for maximal serum-induced SRF activation. MVD7 cells, transfected with SRF reporter 3D.Aluc and RLTK control plasmid, expressed intact VASP or YFP–VASP, together with VASPΔB (0.9 µg). Reporter activity was determined before and after serum stimulation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.