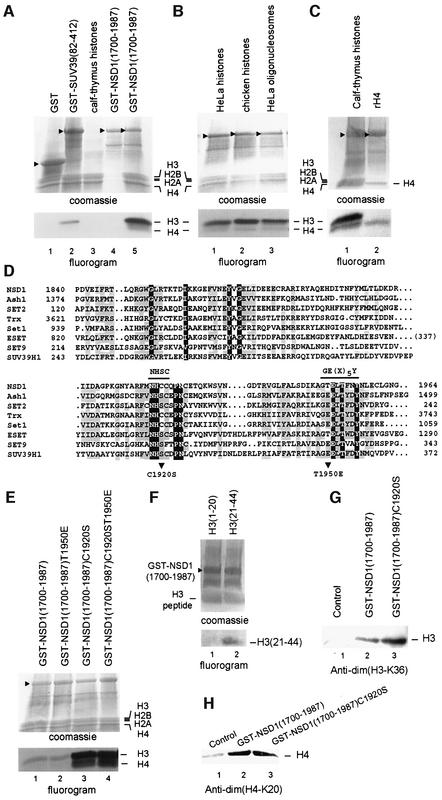
Fig. 6. The NSD1 SET domain has intrinsic HMTase activity with specificity for H3-K36 and H4-K20. (A) Coomassie blue-stained SDS–polyacrylamide gel and corresponding flurorogram of HMTase assays with the indicated GST fusion proteins and a mixture of purified calf thymus histones as substrates. (B) HMTase assays as in (A), except that reactions contained either a mixture of native core histones from HeLa cells (lane 1) or chicken (lane 2), or oligonucleosomes purified from HeLa cells (lane 3), and GST–NSD1(1700–1987) as enzyme. (C) HMTase assays as in (A), except that reactions contained either purified calf thymus histones (lane 1) or recombinant H4 (lane 2), and GST–NSD1(1700–1987) as enzyme. (D) Amino acid alignment of the NSD1 SET domain with other selected SET domains. The sequences were aligned using the CLUSTAL W program and manual adjustment. Invariant amino acids are highlighted in blue. Amino acids conserved in >60% of the proteins are highlighted in yellow. The two conserved amino acid stretches important for the methyltransferase catalytic activity of the SET domain are indicated. Mutations described in this study are indicated below the alignment. (E) The C1920S mutation generated a hyperactive SET domain mutant. Equal amounts of wild-type and mutant GST–NSD1 proteins (top panel) were compared for their HMTase activities (bottom panel) using equal amounts of purified calf thymus histones. (F) HMTase assays as in (A) using GST–NSD1(1700–1987) as enzyme and the indicated N-terminal peptides of H3. (G) Western blot analyses, using anti-dim(H3-K36), of HMTase assays containing recombinant H3 and the indicated GST–NSD1 proteins. (H) Western blot analyses, using anti-dim(H4-K20), of HMTase assays containing recombinant H4 and the indicated GST–NSD1 proteins.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.