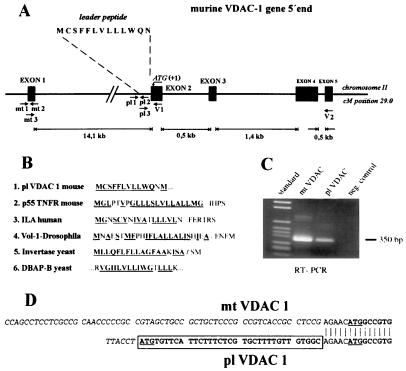
Figure 1.
Expression of alternative mRNAs encoding mt-VDAC-1 and pl-VDAC-1 porins. (A) Schematic representation of the 5′ genomic structure of the murine VDAC-1 gene. pl 1, pl 2, and pl 3 indicate location of primers used for RT-PCR and RACE-PCR. Indicated are the first four exons and their relative lengths. Exon 1 encodes 5′ untranslated RNA of mt-VDAC-1 mRNA. The ORF of mt-VDAC-1 starts 4 bases into the second exon (indicated as residue +1); the ORF of pl-VDAC-1 begins 39 bases 5′ adjacent to this point. kb, kilobase. (B) Comparison of hydrophobic signal leader sequences between pl-VDAC-1 and integral membrane proteins. EMBL data library or GenBank accession numbers are, for p55 tumor necrosis factor, X59238 (27); for activation-dependent T cell mRNA (ILA), L12964 (28); for Drosophila integrin α-subunit (Volado), AF034199 (29); for Saccharomyces cerevisiae SUC2 gene encoding invertase, K03294 (30); and for yeast dipeptidyl aminopeptidase B, X15484 (31). (C) PCR amplification of exons 1–5 of mt-VDAC-1 and of pl-VDAC-1. Primer pairs mt3/V2 and pl3/V2 are indicated in A. Bands of the expected size of 350 bp were amplified and sequenced. Negative control was performed with H2O instead of RNA. (D) Sequence of the longest RACE-PCR products obtained with primer V1. The ATG protein start codon of the previously known mt-VDAC-1 form is underlined; the hydrophobic leader peptide of pl-VDAC-1 is boxed.