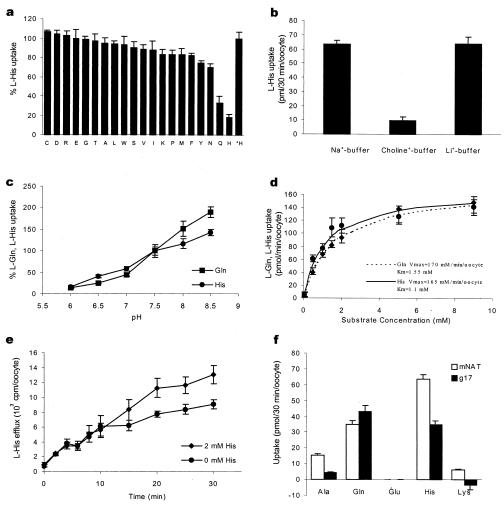
Figure 3.
Functional characterization of mNAT expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. (a) Inhibition of 50 μM l-histidine uptake in oocytes injected with cRNA of mNAT by 5 mM of 20 types of l-amino acids. The percentage values after subtracting controls injected with water are presented as 50 μM l-histidine uptake is defined as 100%. *Bar represents l-histidine uptake in the absence of nonlabeled amino acids. (b) Uptake of 50 μM [3H]histidine was measured using choline+-buffer or Li+-buffer to replace Na+-buffer. (c) pH dependence of l-histidine and l-glutamine uptake. Uptake of 50 μM [3H] l-histidine or l-glutamine was measured with Na+-buffer under indicated pH. (d) Concentration dependence of l-histidine uptake by mNAT. Net uptakes of l-histidine and glutamine were measured at different concentrations (0–10 mM) of l-histidine in Na+-buffer at pH 7.5. Km = 1.1 mM and Vmax = 170 pmol/min/oocyte for histidine, and Km = 1. 55 mM and Vmax= 165 pmol/min/oocyte for glutamine were determined. (e) l-histidine efflux was examined in Na+-buffer and in Na+-buffer containing 2 mM nonradioactive labeled-l-histidine. (f) Uptake rates for l-alanine, l-glutamine, l-glutamate, l-histidine, and l-lysine were determined for oocytes expressing mNAT and human g17.