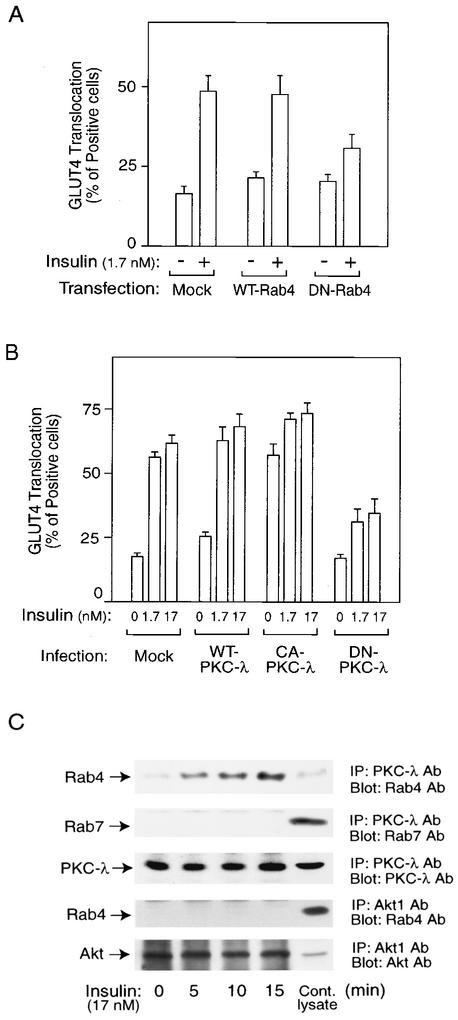
FIG. 1.
Molecular complex with Rab4 and PKC-λ plays a role in insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. (A) Mock control, wild-type Rab4 (WT-Rab4), or dominant-negative Rab4 (DN-Rab4) expression vectors together with an eGFP-GLUT4 expression vector were transiently transfected into 3T3-L1 adipocytes by electroporation. Forty-eight hours after incubation, cells were starved and treated with 1.7 nM insulin for 20 min or received no insulin treatment. GLUT4 translocation was detected by assessing cell surface eGFP fluorescence. The percentage of cells positive for GLUT4 translocation was calculated by counting at least 200 cells at each point. The data represent the means ± standard errors (SE) from three independent experiments. (B) Sixty hours after infection with PKC-λ-expressing adenovirus (MOI, 30 PFU/cell), serum-starved 3T3-L1 adipocytes on coverslips were incubated with or without insulin for 20 min. The percentage of cells positive for GLUT4 translocation was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The data are the means ± SE from three independent experiments. (C) Serum-starved 3T3-L1 adipocytes were stimulated with 17 nM insulin for the indicated time periods, and then cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated (IP) with the anti-PKC-λ or -Akt1 antibody (Ab). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting. These experiments were repeated three times.