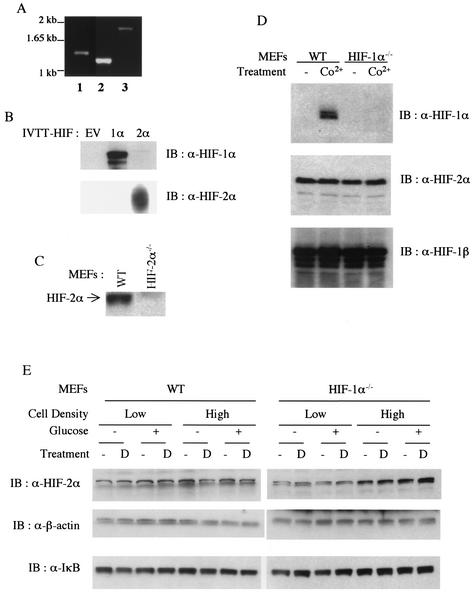
FIG. 1.
Constitutive expression of HIF-2α in T-antigen-transformed mouse embryonic fibroblasts. (A) Reverse transcription-PCR analysis of HIF-2α mRNA in MEFs. Reverse-transcribed first-strand cDNAs from wild-type (WT) MEFs were amplified with primer sets covering the 5′ half (lanes 1 and 2) and the 3′ half (lane 3) of the HIF-2α open reading frame. (B and C) Specificity of mouse monoclonal anti-HIF-1α and rabbit polyclonal anti-HIF-2α antibodies. Polyclonal anti-HIF-2α shows specificity to in vitro-transcribed and -translated (IVTT) mouse HIF-2α (B) and endogenous HIF-2α which is present in wild-type but absent from HIF-2α null cells (C). EV, empty vector. (D) Western blot (IB) analysis of whole-cell extracts of untreated (lanes 1 and 3) and CoCl2-treated (100 μM, 4 h; lanes 2 and 4) wild-type (lanes 1 and 2) and HIF-1α null MEFs (lanes 3 and 4) with anti-HIF-1α (upper), anti-HIF-2α (middle), and anti-ARNT (bottom) antibodies. (E) Effect of glucose deprivation on HIF-2α expression in MEFs at two different seeding densities. Both wild-type and HIF-1α null MEFs were incubated in either high-glucose (4.5 g/liter) or glucose-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium with or without deferoxamine (100 μM; lanes D) for 4 h before being harvested for whole-cell extraction.