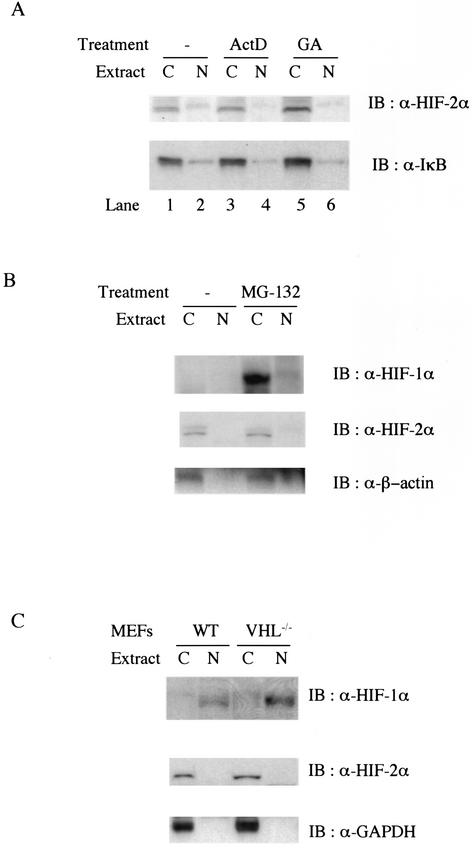
FIG. 4.
(A) Protein expression level and subcellular location of endogenous HIF-2α are not affected by inhibition of transcription or heat shock protein 90 activity. Wild-type MEFs were untreated (lanes 1 and 2) or treated with 10 μg of actinomycin D per ml (ActD, lanes 3 and 4) or 10 μM geldanamycin (GA, lanes 5 and 6). Then 25 μg of either cytoplasmic (lanes C) or nuclear (lanes N) protein was analyzed by Western blot (IB) analysis with anti-HIF-2α (upper panel) or anti-IκB (lower panel) antibodies. (B) Endogenous HIF-2α escapes 26S proteasome-dependent protein turnover in normoxic MEFs. Wild-type (WT) MEFs were treated with 50 μM MG-132 for 4 h before being harvested. Then 25 μg of either cytoplasmic or nuclear protein was analyzed for Western blot analysis with anti-β-actin (lower panel) or anti-HIF-2α (middle panel), and the same membrane was reprobed with anti-HIF-1α (upper panel). (C) Expression and subcellular location of HIF-1α and -2α in wild-type and VHL null primary MEFs. Cell extracts from wild-type and VHL null primary MEFs were analyzed by Western blot analysis with anti-HIF-1α (upper panel), anti-HIF-2α (middle panel), and anti-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (lower panel).