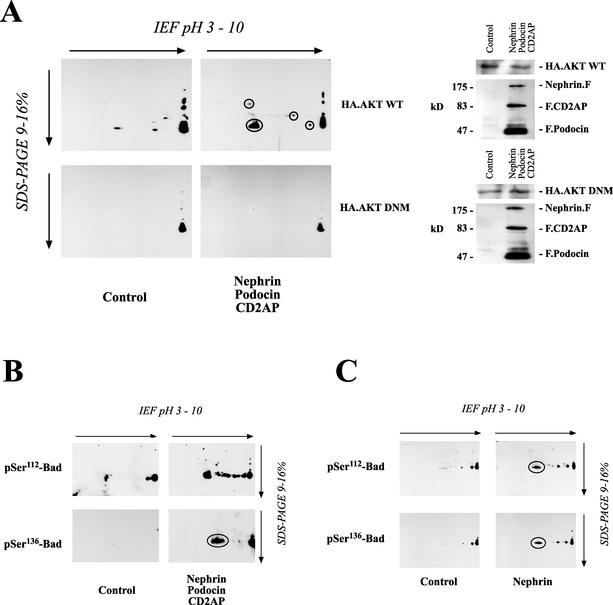
FIG. 5.
Identification of downstream target proteins of nephrin-CD2AP-podocin-stimulated AKT activity. (A) Equal amounts of protein from HEK 293T cells transfected with either a vector control (9 μg of plasmid) or nephrin (3 μg), CD2AP (3 μg), and podocin (3 μg) in combination with either wild-type (WT) AKT or a dominant-negative mutant (DNM) were separated on a 2-D gel. To analyze the formation of active 14-3-3 binding sites associated with the nephrin-CD2AP-podocin-stimulated AKT activity, cell lysates were transferred onto PVDF membranes and immunoblotted with a phosphospecific antiserum raised against the 14-3-3 mode 1 binding motif (left). Lysates from these cells showed comparable AKT expressions (right). F, FLAG; IEF, isoelectric focusing. (B and C) The proapoptotic Bcl2 family member Bad is regulated by AKT-dependent phosphorylation on serine-112 (pSer112) and serine-136. Equal amounts of protein from HEK 293T cells expressing either a vector control (9 μg of plasmid) or nephrin (3 μg), CD2AP (3 μg), and podocin (3 μg) in combination with wild-type AKT were separated on a 2-D gel. Nephrin, podocin, and CD2AP induced the phosphorylation of endogenous Bad on both regulatory sites, serine-112 and serine-136, as demonstrated by the phosphospecific antiserum (B), whereas AKT expression was not influenced (not shown). The same result, although with a weaker effect, could be demonstrated with nephrin alone (C). Circles indicate spots identified with phosphospecific antiserum against 14-3-3 mode 1 binding motif (A) or with phosphospecific antisera against Bad (B and C).