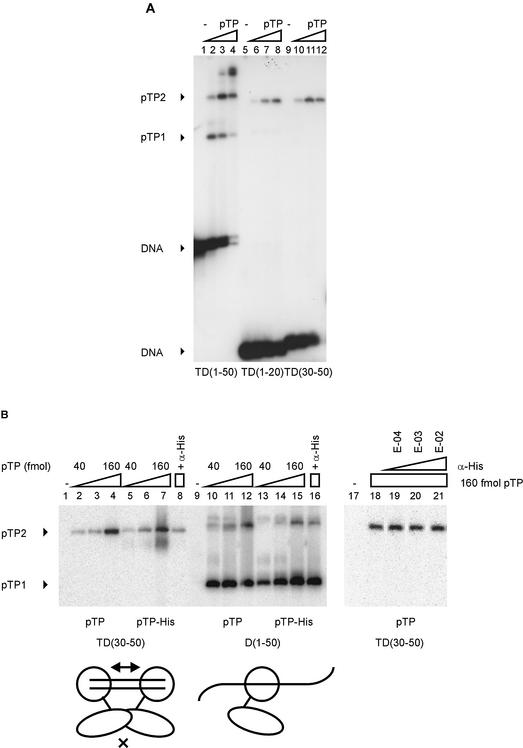
Figure 2.
pTP dimerizes specifically on small DNA duplexes. (A) pTP binding to TD(30–50) was studied using EMSA. Lanes 1–4, TD(1–50); lanes 5–8, TD(1–20); lanes 9–12, TD(30–50). Lanes 1, 5 and 9, free probe; lanes 2, 6 and 10, 40 fmol pTP; lanes 3, 7 and 11, 80 fmol pTP; lanes 4, 8 and 12, 160 fmol pTP. Free DNA, pTP1 and pTP2 complexes are indicated. (B) Comparison of pTP and pTP-His binding to TD(30–50) and D(1–50). Lanes 1–8 and 17–21, TD(30–50); lanes 9–16, D(1–50). Lanes 2–4 and 10–12, 40, 80 and 160 fmol pTP; lanes 5–7 and 13–15, 40, 80 and 160 fmol pTP-His. Lanes 4, 16 and 18–21, 160 fmol pTP + α-His antibody added during preincubation at E-04 (lane 19), E-03 (lane 20) or E-02 dilution (lanes 8, 16 and 21). pTP1 and pTP2 complexes are indicated; free DNA was run off the gel to obtain large separation of the pTP1 and pTP2 (and potential pTP-His/antibody) complexes. Schematically indicated at the bottom of the figure are two pTP-His (large circle with extending line)/α-His (small oval) complexes binding to the short DNA duplex TD(30–50) or a single complex bound to D(1–50). E-02, 1:100 dilution; E-03, 1:1000 dilution; E-04, 1:10 000 dilution.