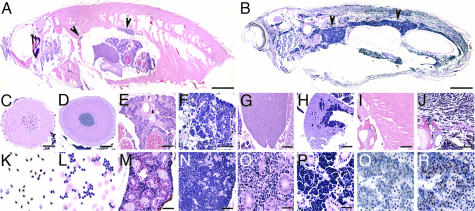
Fig. 3.
Leukemic features of TEL-AML1 transgenic zebrafish. (A and B) H&E stain of sagittal sections from wild-type (A) and an F1 XEF-EGFP-TA transgenic zebrafish (B), with diffuse infiltrates of basophilic blast-like cells, most dense in the kidney region (arrows indicate head and tail kidney). Leukemic cells infiltrated distal organs including the brain (D), ovary (F), liver (H), and muscle (J), compared with wild-type sections from these organs (C, E, G, and I). Peripheral blood smear from wild-type fish (K) showing normal nucleated RBCs, lymphocytes, and a monocyte, whereas a leukemic blood smear (L) shows clusters of lymphoblasts. The kidney section revealed complete infiltration of the marrow between the tubules shown in low (N) and high (P) power, compared with wild-type (M and O). (Q and R) Leukemic cells express EGFP-TEL-AML1. (Q) No staining without the primary anti-EGFP antibody. (R) TEL-AML1 lymphoblasts showed strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining with anti-EGFP antibody (arrows). (Scale bars, 3 mm in A and B; 100 μm in C–M and O; and 50 μm in N, P and Q and R.)