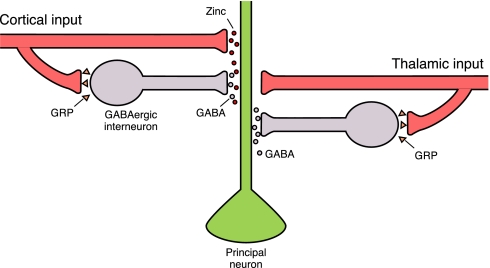
Fig. 6.
A model for input-specific modulation of GABAergic inhibition by synaptically released zinc in the lateral amygdala. GRP is released by neurons projecting to the LA (see ref. 4). GRP binds to receptors on interneurons, leading to their enhanced firing and stronger inhibition of principal neurons. Glutamatergic cortico-amygdala afferents also contain Zn2+, whereas no Zn+-containing cells are detected in the thalamic CS areas also sending glutamatergic projections to the LA. Input-specific suppression of feed-forward GABAergic inhibition of principal neurons in the LA by synaptically released Zn2+ may control spatial specificity of LTP in fear conditioning pathways.