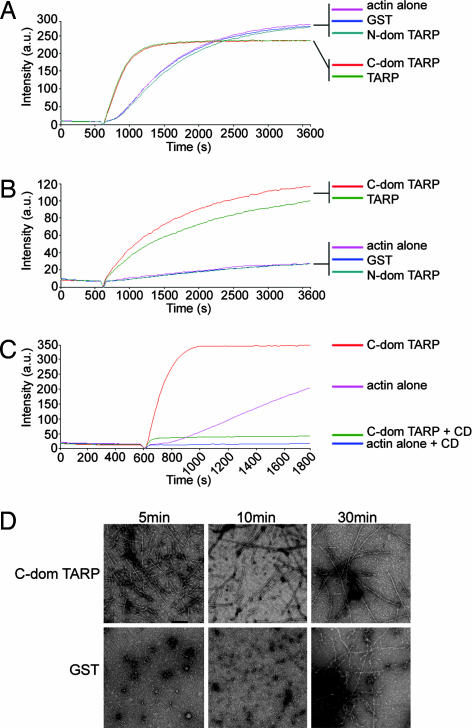
Fig. 2.
TARP promotes actin polymerization. (A) Pyrene actin polymerization in the presence of GST-TARP fusions. GST-TARP fusions representing the entire protein (TARP), C-terminal domain of TARP (C-dom TARP), or N-terminal domain of TARP (N-dom TARP) were incubated with 1 μM monomeric pyrene-labeled actin. A TARP-mediated increase in actin polymerization after the addition of polymerization buffer at 600 sec was measured as arbitrary fluorescence intensity (Intensity a.u) over time (seconds) with excitation and emission wavelengths of 365 and 407 nm, respectively. Purified GST (GST) and pyrene actin alone (actin alone) served as negative controls. (B) TARP-mediated actin polymerization occurs in the presence of HeLa extracts. Pyrene actin polymerization as described in A with the addition of 10 μg of HeLa extracts. (C) CD inhibits actin filament growth initiated by TARP. Pyrene assay as in A with the addition of 1 μM CD added to the C-terminal domain of TARP (C-dom TARP + CD) and actin control (actin alone + CD). (D) Pyrene-conjugated actin was visualized by transmission electron microscopy after initiation of polymerization. Actin filaments generated in the presence of the C-terminal domain of TARP (C-dom TARP) or GST control (GST) were collected at 5, 10, and 30 min postpolymerization initiation and stained with 1% uranyl-acetate. (Scale bar, 0.1 μm.)