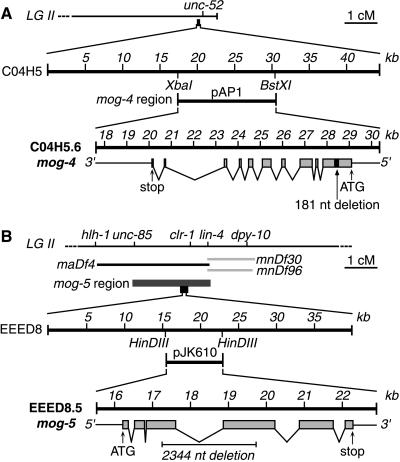
Figure 1.
Cloning mog-4 and mog-5. (A) mog-4. (A, Top) Genetic map of mog-4 region at right end of chromosome II (6). (A, Middle) Cosmid C04H5 resides ≈100 kb to the left of unc-52. The 12.8-kb subclone of C04H5, called pAP1, is predicted to contain only one transcript, C04H5.6. (A, Bottom) Exon/intron structure of C04H5.6, as predicted by Genefinder and confirmed by cDNA analysis (see Material and Methods). The 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR, thin lines; coding regions of exons, gray boxes; introns, lines joining exons; predicted initiation (ATG) and stop codons are indicated. The pAP2 plasmid contains a 181-nt deletion (black box) from position +582 to +763 in the mog-4 cDNA; this deletion shifts the reading frame and results in a premature stop codon. (B) mog-5. (B, Top) Genetic map of mog-5 region in the center of chromosome II (ref. 6 and this work). Genetic mapping (see Materials and Methods) placed mog-5 in a region corresponding to 2.4 cM or ≈30 cosmids on the physical map. (B, Middle) The EEED8 cosmid resides within the mog-5 region. The pJK610 subclone of EEED8 is 7.4 kb and contains only EEED8.5, the transcript predicted to encode a DEAH-box protein. (B, Bottom) Exon/intron structure of EEED8.5, as predicted by Genefinder and confirmed by cDNA analysis (see Material and Methods). Diagram represented as in Fig. 1A. The pJK611 plasmid contains a 2,344-nt deletion from position 974–2,056 in the mog-5 cDNA [or 1,200–3,544 in the mog-5 genomic fragment]; this deletion removes parts of the third and fourth exons but retains the reading frame.