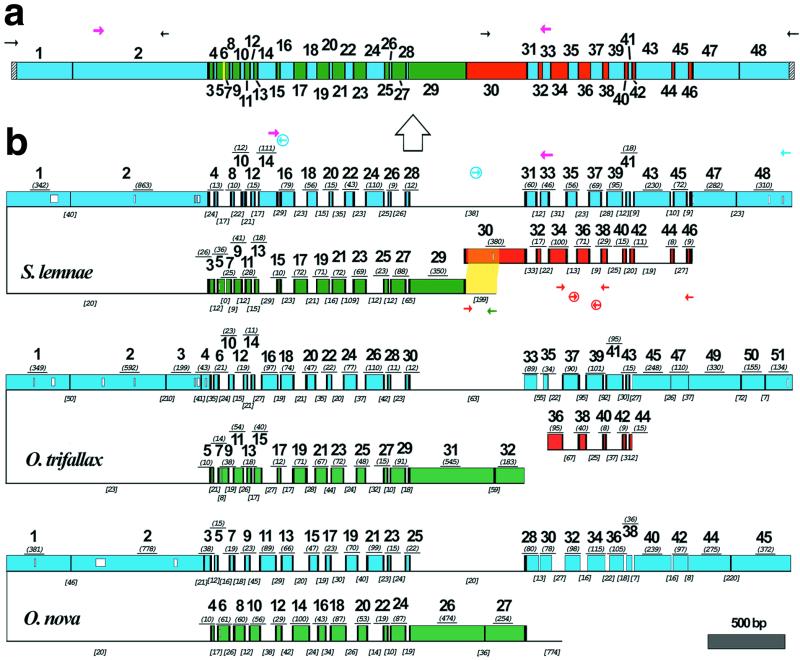
Figure 1.
(a) A schematic map of the macronuclear DNA-polymerase α gene of S. lemnae. The 48 MDS are shown as colored boxes. Green and blue MDSs are both present on the major locus, but in opposite orientation. Red MDSs are derived from the minor locus. The yellow MDS is missing. Pointer sequences are indicated by black vertical bars, telomeres by hatched bars. PCR primers indicated by small arrows; degenerate primers, in magenta, were based on an alignment of this gene in 10 hypotrich species (33). The macronuclear copy is derived from the micronuclear copy (large arrow). (b) A schematic alignment of the micronuclear genes encoding the large catalytic subunit of DNA-polymerase α in S. lemnae, O. trifallax (7), and O. nova (6), with MDSs aligned based on predicted amino acid sequences; open boxes within MDSs indicate gaps in alignment. MDSs are drawn to scale with the length (excluding pointer sequences when available) underlined in italics and parentheses. Green and blue MDSs are encoded on opposite strands of the major locus, indicated by the inversion. Red MDSs are derived from the minor locus. Black vertical bars indicate pointers. IESs are indicated by thin lines, not to scale, but IES length is given in italics and brackets. IES-specific primers are circled. The yellow highlighted region indicates 193/199 bp overlap between the IES that marks the 5′ end of the major locus and MDS 30 in the minor locus of S. lemnae.