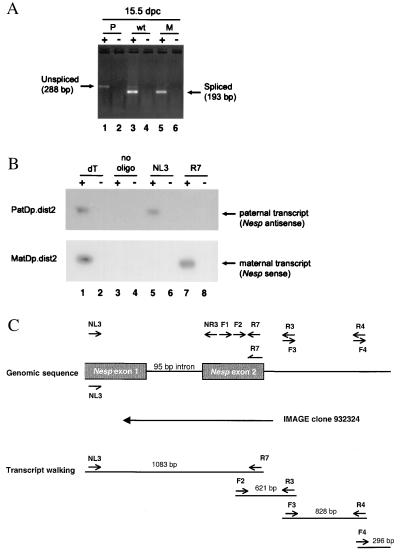
Figure 2.
Identification of an imprinted antisense transcript for Nesp. (A) RT-PCR demonstrating the differential expression of Nesp transcripts in 15.5-dpc embryos. Oligo(dT)-primed cDNA was derived from 15.5-dpc PatDp.dist2 (P), MatDp.dist2 (M), and wild-type sib (wt) embryos. Twenty-five cycles of amplification were performed by using the primers NL3 and NR3. The arrows indicate the Nesp 193-bp spliced and 288-bp unspliced PCR products. RT reactions were carried out in the presence (+) and absence (−) of reverse transcriptase. (B) Southern hybridization of strand-specific RT-PCR products demonstrating that the paternally expressed unspliced isoform lies antisense to Nesp. The first lane is a control RT, using oligo(dT) to show the presence of a product, and the third lane is a negative control for RT without exogenous primer to show the absence of priming by endogenous factors in the RNA preparations. Primer NL3 is specific for the antisense transcript, and R7 is specific for the sense strand. PCR was performed by using primers F1 and R7, which lie 3′ of the intron in Nesp exon 2; 35 cycles were required to detect the less abundant paternal transcript in PatDp.dist2, and 25 cycles were required for the more abundant maternal transcript in MatDp.dist2. The probe was a 229-bp PCR product derived from cDNA extending from primer F2 to exon 2 of Gnas. (C) Diagram showing the approximate position of the primers on genomic sequence (accession nos. AJ245401 and AJ251480). The reverse transcriptase primers (half-arrowheads) specific for the antisense and sense are shown above and below the map, respectively; PCR primers are designated by normal arrows; primer sequence is given in Methods. The approximate position of the IMAGE clone is shown together with PCR products from transcript walking by RT-PCR. The 296-bp product was isolated by RACE. The figure is not to scale.