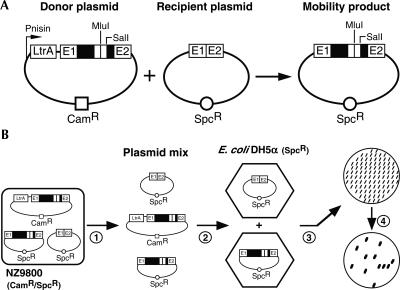
FIGURE 1.
Ll.LtrB mobility assay and mobility efficiency scoring. (A) Two-plasmid Ll.LtrB mobility assay. The assay consists of co-transforming both intron donor and recipient plasmids into NZ9800 L. lactis cells and monitoring the appearance of mobility products. The intron donor plasmid (pLE1-based, CamR) harbors various Ll.LtrB constructs, expressing LtrA in trans, under the control of the nisin-inducible promoter (Pnis). The recipient plasmid (pMNHS, SpcR) contains the intron homing site (E1/E2). Upon nisin induction, the Ll.LtrB intron can move from the donor to the recipient plasmid, generating mobility products. The positions of the engineered SalI and MluI restriction sites, present within the intron, are denoted. The remaining 5′ and 3′ ltrA sequences within Ll.LtrB are represented by empty boxes. (B) Scoring of intron mobility efficiency by colony patch hybridization. Plasmid mixes (donor plasmid, recipient plasmid, and mobility products) from independent mobility assays (panel A) are recovered (step 1) and transformed into E. coli DH5α cells (LB/Spc) (step 2). For each mobility assay, 100 colonies are patched on an LB/Spc plate (step 3), transferred onto a nylon membrane, and hybridized with an intron-specific 32P-labeled probe (step 4). Therefore, the ratio of recipient plasmids that received the intron is calculated.