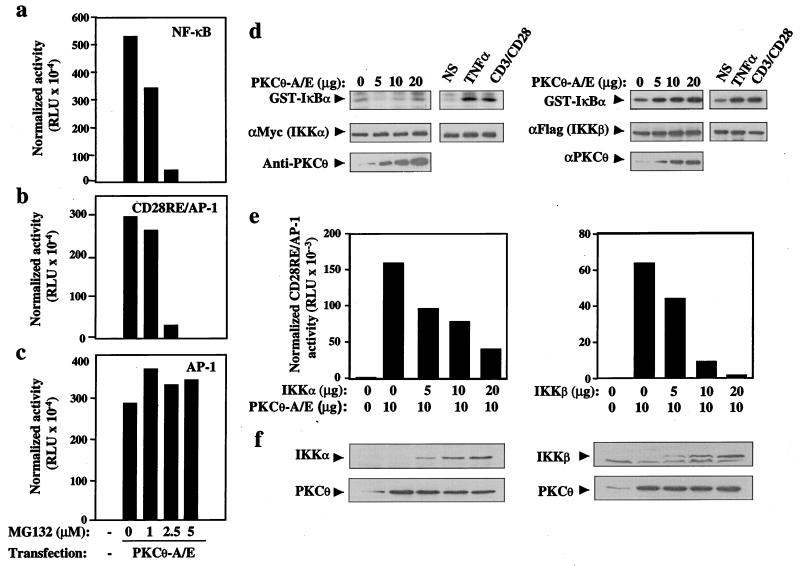
Figure 5.
NF-κB activation induced by PKCθ is mediated by IKKβ/IκBα. Jurkat cells were transfected with an empty vector (−) or constitutively active PKCθ (10 μg) together with NF-κB-Luc (a), CD28RE/AP-1-Luc (b), or AP-1-Luc (c) reporter constructs (5 μg each). The cells were cultured for 16 h with the indicated concentrations of MG132 and lysed, and luciferase activity was quantified. (d) Jurkat cells were transfected with wild-type IKKα (5 μg) or IKKβ (2 μg) together with an empty vector (0) or increasing amounts of constitutively active PKCθ. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies or with TNFα for 10 min. Immunoprecipitated IKKα or IKKβ were subjected to an in vitro kinase assay. Phosphorylated glutathione S-transferase-IκBα/1–62 was detected by autoradiography (Top). The same membrane was immunoblotted with anti-c-Myc or anti-Flag antibodies (Middle). (Bottom) The expression level of PKCθ-A/E. (e) Jurkat cells were transfected with an empty vector or with constitutively active PKCθ (10 μg) in the absence or presence of increasing amounts of kinase inactive IKKα or IKKβ mutants, together with a CD28RE/AP-1-Luc reporter (5 μg). After 24 h, cells were lysed and normalized luciferase activity was determined. (f) The expression level of the transfected IKKs or PKCθ was assessed by Western blotting using c-Myc- (IKKα), Flag- (IKKβ), or PKCθ-specific antibodies.