Figure 3.
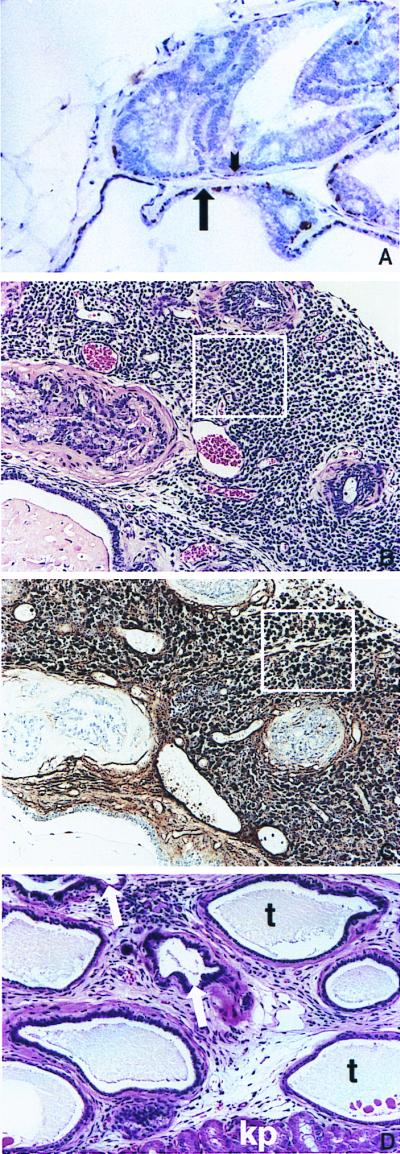
(A) Staining for endogenous K5 in the basal cell layer in the ventral prostate of a BK5.IGF-1 mouse. Note the lack of staining for K5 in the dysplastic acinus in the upper half of the picture (short arrow points to area devoid of K5 staining) whereas the more normal acinus in the lower portion of this panel (long arrow) still retains K5 staining. Keratin 5 was detected by using a rabbit polyclonal anti-mouse K5 antibody (Covance, Berkeley, CA) (described in ref. 47). (B) Small cell carcinoma from a 14-month-old BK5.IGF-1 mouse. Area enclosed in box is representative of this lesion. (C) Immunohistochemical staining for serotonin in a section from the small cell carcinoma shown in B. Area enclosed in box shows representative cells darkly stained for serotonin. To detect neuroendocrine cells, slides were treated with protease and were stained with mouse monoclonal anti-seratonin antibody (Dako) according to the manufacturer's instructions. (D) Atypical acini growing in the kidney capsule of an athymic mouse. Arrows point to atypical acini. Also note the unusual tubular structures (t) and the kidney parenchyma (kp) present in this section. (A–D, ×150.)
