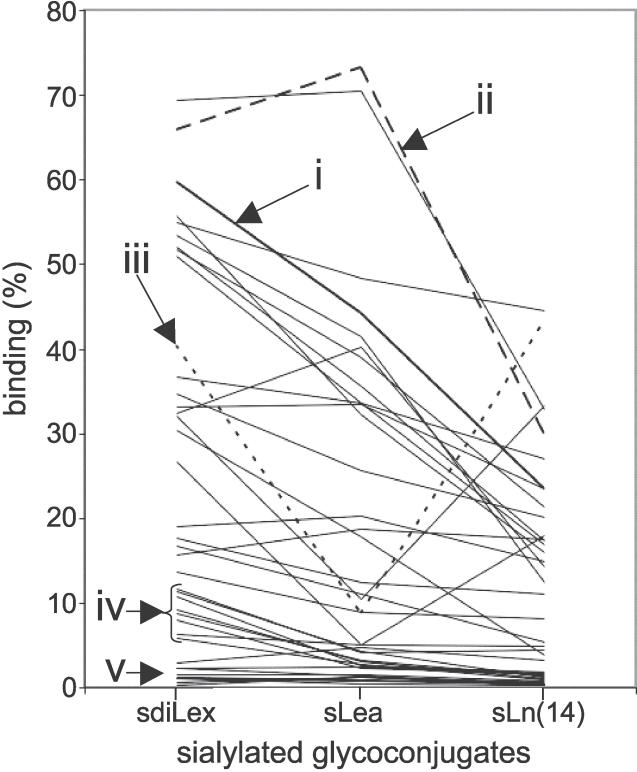
Figure 5. Different Sialyl-Dependent Binding Modes of H. pylori Identified by Use of sdiLex, sLea, and sLn Conjugates.
A total of 39 Swedish clinical isolates were investigated for detailed sialyl-dependent binding properties. Representatives of the different binding modes for 125I-labeled sialylated glycans are illustrated in the diagram: (i) (in thick line) binds efficiently to all three sialylated glycans with preferential binding to sdiLex; (ii) binds to all three sialylated glycans, with better binding to sLea (“Λ-shaped” hatched line); (iii) binds preferentially to sdiLex and sLn(14) (“V-shaped” dotted line); (iv) binds preferentially to sdiLex but exhibits only modest binding for sLea and sLn(14) sialyl conjugates; and (v) binds modestly for all sialyl conjugates (<5% bound conjugate). The y axis gives the percentage of bound conjugate.