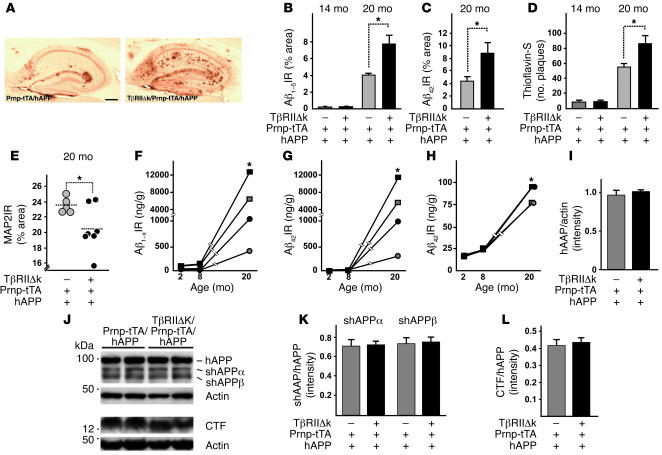
Figure 3. Decreased neuronal TGF-β signaling in old hAPP mice increases Aβ levels, amyloid deposition, and dendritic degeneration.
(A) Representative images of hippocampi of 20-month-old TβRIIΔk/Prnp-tTA/hAPP and Prnp-tTA/hAPP mice stained with an antibody against Aβ42. Scale bar: 500 μm. (B–D) Quantification of immunoreactive area occupied by staining with antibody against Aβ1–5 (B), antibody against Aβ42 (C), and thioflavin-S (D) of sagittal sections from 14- and 20-month-old TβRIIΔk/Prnp-tTA/hAPP and Prnp-tTA/hAPP mice (n = 5–7 mice per genotype). (E) Expression of TβRIIΔk in neurons of aged hAPP mice reduced MAP2 immunoreactivity in the hippocampus. Sagittal brain sections of 20-month-old mice were stained with MAP2, and percent immunoreactive area of the neuropil was determined by confocal microscopy and computer-aided image analysis. Each symbol represents 1 mouse. (F–H) Quantification of Aβ1–x (F), Aβ42 (G), and percent Aβ42 (H) via ELISA in hippocampus (squares) and cortex (circles) of TβRIIΔk/Prnp-tTA/hAPP (black symbols) and Prnp-tTA/hAPP (gray symbols) mice aged 2, 8, and 20 months (n = 5–7 mice per genotype). Note the cutoff in the y axes. (I–L) Signal intensities of total APP (I), shAPPα and shAPPβ (K), and CTFs (L) were quantified and normalized against total APP levels (K and L) or protein amounts loaded (I). Representative Western blots (J) of cell pellets (hAPP, CTF, and actin) or supernatants (shAPPα and shAPPβ) probed with antibodies against total APP, CTFs, actin, shAPPα, and shAPPβ. *P < 0.05; Student’s t test (B–D and F–H), Tukey-Kramer test (E).