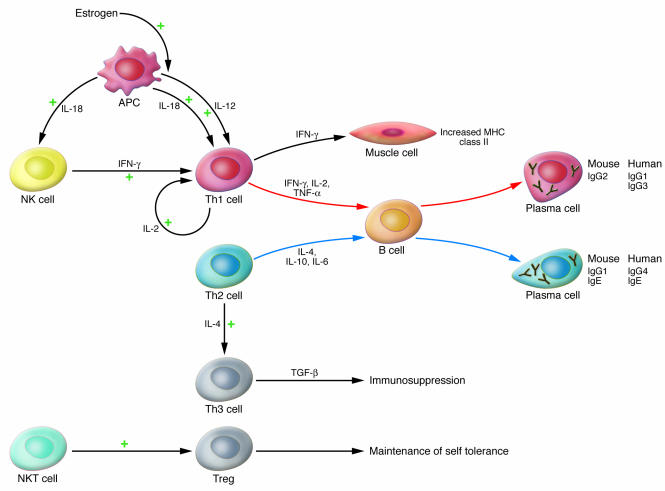
Figure 3. Cytokine network and cells involved in the pathogenesis and immunoregulation of MG.
Th1 cytokines stimulate production of IgG subclasses that bind and activate complement effectively, whereas Th2 cytokines stimulate the production of Ig classes and IgG subclasses that do not. The Th2 cytokine IL-4 is also a differentiation factor for Th3 cells, immunosuppressive cells that secrete TGF-β. The Th1 cytokine IFN-γ stimulates expression of MHC class II molecules on the muscle cell membrane, thus facilitating presentation of muscle AChR. The IL-18 secreted by APCs favors the differentiation of Th1 cells both directly and indirectly through the action of NK cells. CD1-d–restricted NKT cells can activate Tregs, thereby inhibiting autoimmune processes. See text for further details.