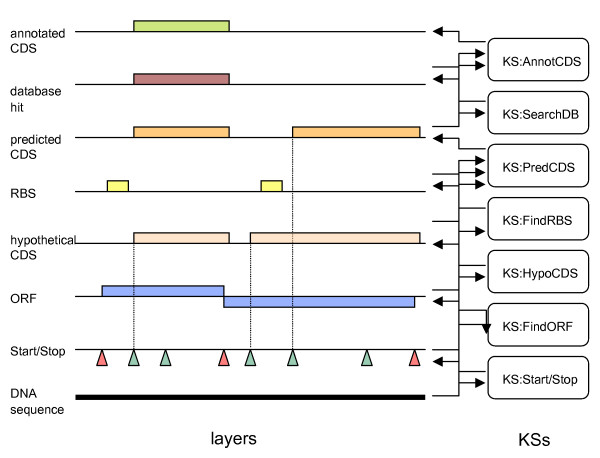
Figure 3.
Example of layers and knowledge sources implementing the basic annotation strategy of Figure 2. The layers are named after the type of objects they accommodate. Knowledge sources take objects from one or several layers as input and produce new objects on upper layers. KS:Start/Stop and KS:FindRBS directly work on the raw DNA sequence to locate respectively the Start and Stop triplets and the ribosome binding sites (RBS). KS:FindORF builds ORFs from the Starts and Stops locations. KS:HypoCDS computes a hypothetical CDS by retaining the leftmost in-frame Start within an ORF. KS:predCDS validates a hypothetical CDS (or possibly modifies its beginning) because of the existence of an RBS. The resulting CDS is placed on the predicted CDS layer. The final step consists in searching sequence databases for similarities with known genes to finally ascertain annotated CDSs.