FIG. 1.
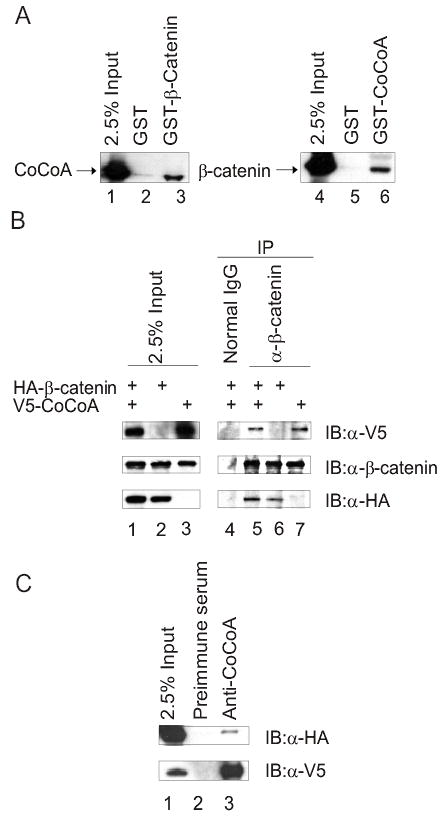
CoCoA interacts with β-catenin in vitro and in vivo. (A) Plasmids encoding HA-tagged CoCoA or β-catenin were transfected into COS-7 cells. Cell lysates were collected 48 h after transfection and incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads containing GST (lanes 2 & 5), GST-β-catenin (lane 3), or GST-CoCoA (lane 6) for GST pull-down assays. Bound proteins were eluted with SDS sample buffer and analyzed by immunoblot with antibodies against the HA-epitope tag. A portion of the amount of cell lysate incubated with beads was loaded as control (2.5% Input, lanes 1 & 4). (B) Co-immunoprecipitation was performed with extracts of COS-7 cells transfected with 5βg each of plasmids encoding HA-tagged β-catenin and V5-tagged CoCoA, as indicated. After 48 h cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-β-catenin antibody or normal rabbit IgG as control and analyzed by immunoblots using anti-V5 antibody (top panel), anti-β-catenin antibody (middle panel), or anti-HA antibody (bottom panel). (C) Co-immunoprecipitation was performed as in B, using anti-CoCoA antisera for immunoprecipitation and anti-HA antibody (top panel) or anti-V5 antibody (lower panel) for immunoblots.
