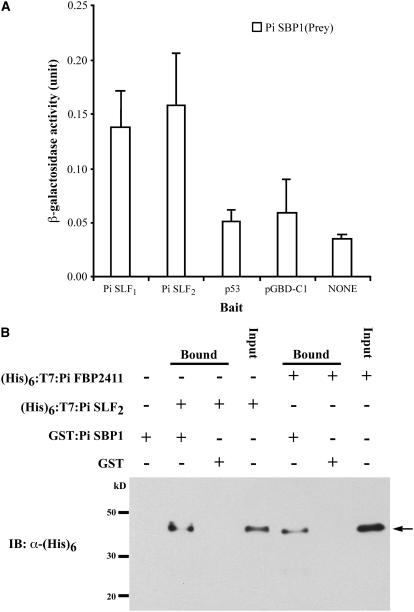
Figure 2.
Analyses of Interactions of Pi SBP1 with Pi SLF1 and Pi SLF2.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assay. Pi SBP1 (in prey vector pGAD-C1) along with three bait constructs containing Pi SLF1, Pi SLF2, or p53, and with the bait vector pGBD-C1, were separately cotransformed into the yeast strain SFY526, and the transformants were used for the assay. Pi SBP1 (in pGAD-C1) alone was also transformed into SFY526 (NONE). The β-galactosidase activities shown are mean values + sd measured from six independent yeast transformants.
(B) In vitro binding assay. Pi SLF2 and Pi FBP2411 (an F-box protein likely encoded by a gene unlinked to the S-locus) were expressed as (His)6:T7:Pi SLF2 and (His)6:T7:Pi FBP2411, respectively, and the purified proteins were incubated separately with GST:Pi SBP1-bound Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow resin. As negative controls in this figure and in Figures 4B, 6B, and 6C, the same amount of GST:Pi SBP1-bound resin used in each binding assay was incubated without any (His)6:T7-tagged protein, and GST-bound resin was incubated with the (His)6:T7-tagged protein, as indicated, under the same conditions used in each binding assay. The bound proteins (arrow) were eluted and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) using an anti-(His)6 antibody. Input lanes in this figure and in Figures 4B, 5C, 5D, 6B, and 6C contain a fraction of the (His)6:T7-tagged protein, as indicated, used in the binding assay.