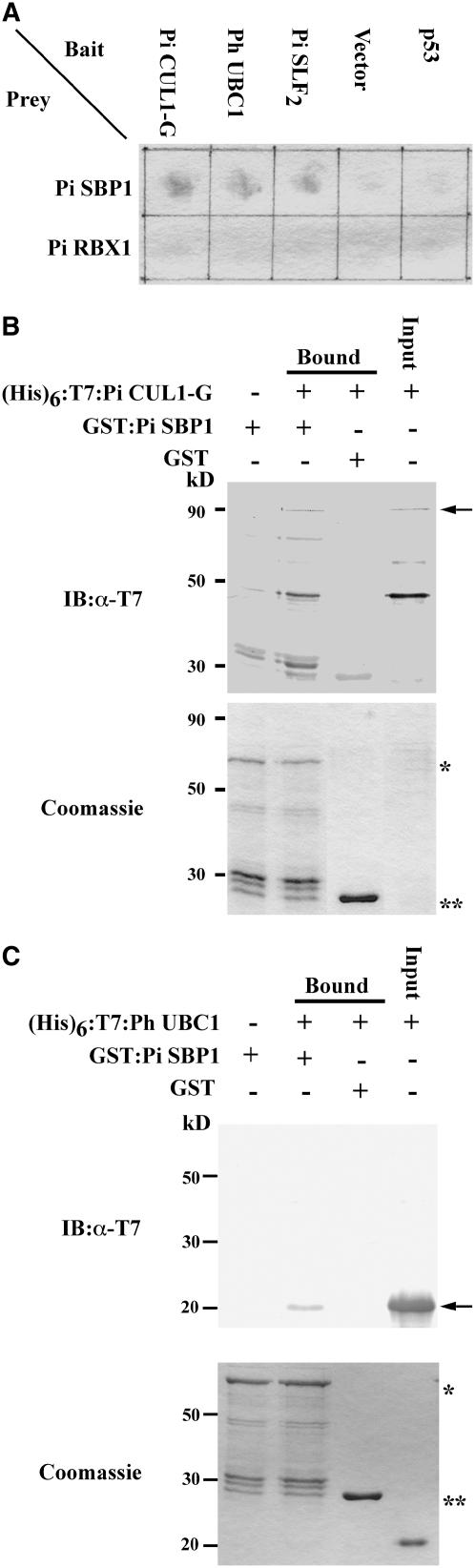
Figure 6.
Interactions of Pi SBP1 with Pi CUL1-G and Ph UBC1.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assay showing that Pi SBP1, but not Pi RBX1, interacts with Pi CUL1-G, Ph UBC1 (an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme of P. hybrida), and Pi SLF2. The β-galactosidase activity assay was performed as described in the legend to Figure 1 except that the filter paper was incubated for 5 h at 30°C.
(B) In vitro binding assay of the interaction between Pi SBP1 and Pi CUL1-G. Purified (His)6:T7:Pi CUL1-G was tested for its interaction with GST:Pi SBP1 in the binding assay as described in the legend to Figure 2B. Top panel, immunoblot (IB). The bound (His)6:T7:Pi CUL1-G was detected by the anti-T7 tag antibody and is indicated with an arrow. The other bands with lower molecular masses cross-reacted with the antibody and were detected only after a long exposure of the blot. Bottom panel, Coomassie blue staining of a duplicate gel of that used in immunoblotting. The asterisk indicates the GST:Pi SBP1 band, and the double asterisks indicate the GST band.
(C) In vitro binding assay of the interaction between Pi SBP1 and Ph UBC1. Purified (His)6:T7:Ph UBC1 was used along with GST:Pi SBP1 in the assay as described in the legend to Figure 2B. The bound (His)6:T7:Ph UBC1 was detected by an anti-T7 tag antibody. Top panel, immunoblot. The arrow indicates the (His)6:T7:Ph UBC1 band. Bottom panel, Coomassie blue staining of a duplicate gel of that used in immunoblotting. The asterisk indicates the GST:Pi SBP1 band, and the double asterisks indicate the GST band.