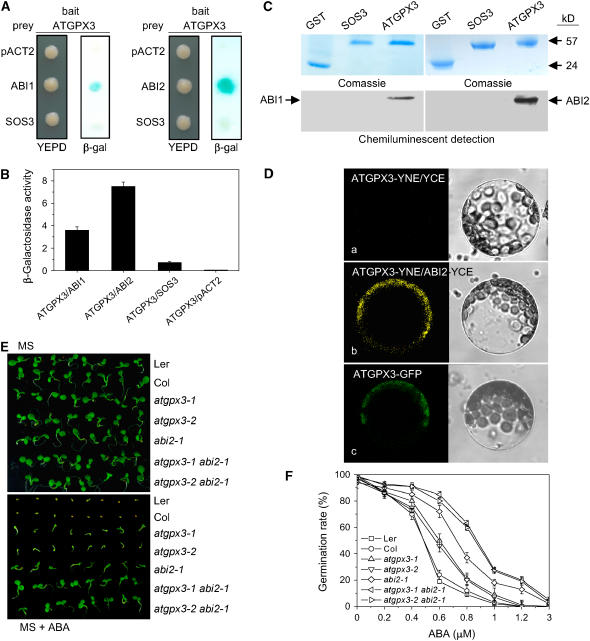
Figure 5.
ATGPX3 Specifically Interacts with ABI2 and ABI1.
(A) ATGPX3 strongly interacted with ABI2 or ABI1 in the yeast two-hybrid system. Yeast strains containing pAS-ATGPX3 as bait and pACT-ABI2/1 as prey were grown on YEPD medium lacking Trp and Leu for 48 h (left panel) and were assayed for LacZ expression by a filter-lift assay (right panel). pACT-SOS3 and the empty prey vector were used as negative controls. Blue color indicates interaction. β-gal, β-galactosidase activity.
(B) Quantitative analysis of β-galactosidase activity of the yeast strains in liquid culture showing the interaction between ATGPX3 and ABI2 or ABI1 and with the control partner SOS3. Values are means of data from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate sd.
(C) Biotinylated Lys-labeled ABI1/2 protein was pulled down by GST-ATGPX3 but not by GST-SOS3. GST was used as a negative control.
(D) In vivo interaction between ATGPX3 and ABI2 as determined using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. a, control (SYNE-ATGPX3 and SYCE); b, the YFP signal in the cytoplasm indicates a positive interaction between ATGPX3 and ABI2; c, the ATGPX3-GFP protein is localized in the cytoplasm. Left panel, fluorescence images under confocal microscopy; right panel, bright-field images of the cell.
(E) The phenotypes of atgpx3 and abi2 single mutants and double mutants (atgpx3-1 abi2-1 and atgpx3-2 abi2-1). F2 seeds from the crosses between the respective mutants were planted on MS agar medium (top plate) or MS agar medium supplemented 0.5 μM ABA (bottom plate) and allowed to grow for 2 weeks before the photographs were taken. Col, Columbia; Ler, Landsberg erecta.
(F) Comparisons of germination rates of the wild type, atgpx3-1, atgpx3-2, abi2-1, and the double mutants atgpx3-1 abi2-1 and atgpx3-2 abi2-1 after exposure to different concentrations of ABA for 10 d. Values are means ± sd of three independent experiments (>120 seeds per point).