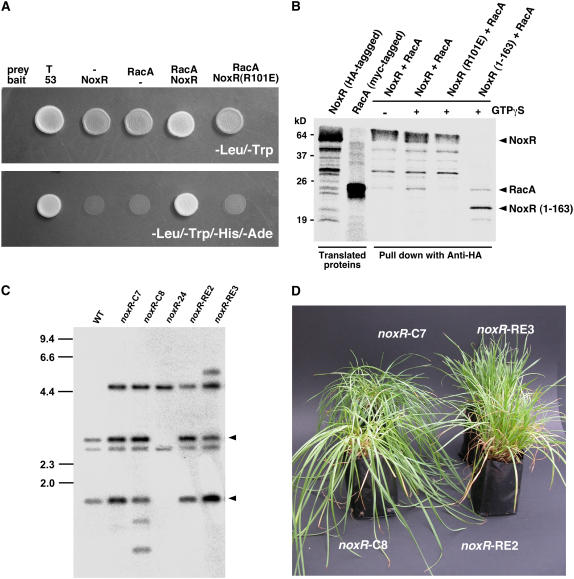
Figure 8.
NoxR Requires RacA for Functional Activity.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assay of the interaction between E. festucae NoxR and RacA. Yeast strain AH109 was transformed with prey and bait vectors as indicated and plated on SD medium lacking Leu and Trp (top panel; -Leu/-Trp) or lacking Leu, Trp, His, and adenine (bottom panel; -Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade). Growth on the latter indicates an interaction between bait and prey. T, SV40 large T-antigen; 53, murine p53.
(B) In vitro pull-down assay showing interaction between E. festucae NoxR and RacA. Autoradiograph of [35S]-labeled in vitro cell-free translation products using noxR and racA plasmids as templates and proteins pulled down with anti-HA, with or without 100 μM GTPγS, following incubation of NoxR and RacA in vitro translation products. The molecular mass of protein standards, in kilodaltons, is shown at the left of the figure.
(C) Autoradiograph of DNA gel blot of BglII-EcoRI genomic digest (2 μg) of E. festucae wild type, noxR mutant complemented with wild-type noxR plasmid pPN109, strains PN2483 (noxR-C7) and PN2484 (noxR-C8), noxR deletion strain PN2497 (noxR-24), noxR mutant not complemented with plasmid pPN110 (noxR with the R101E mutation), and strains PN2485 (noxR-RE2) and PN2486 (noxR-RE3) probed with [32P]-labeled noxR replacement insert amplified from pPN108 with primers pII99-2 and pII99-3. Arrowheads identify DNA fragments derived from the noxR complementation construct. Sizes in kilobases of HindIII-digested λ DNA markers are indicated at left.
(D) Phenotype of perennial ryegrass plants infected with E. festucae noxR mutant transformed with either a wild-type copy of noxR, strains PN2483 (noxR-C7) and PN2484 (noxR-C8), or with noxR containing an R101E mutation, strains PN2485 (noxR-RE3) and PN2486 (noxR-RE2).