Abstract
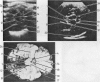
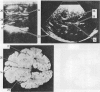
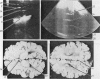
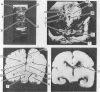
A method for systematic scanning of the neonatal brain with real-time ultrasound is described, and the linear array is compared with mechanical sector scanners. Anatomical landmarks recognised on axial, coronal, and parasagittal scans are verified by comparison with brain slices at necropsy. A prospective study of 50 infants admitted consecutively to the neonatal unit at this hospital showed intraventricular haemorrhage in 18 (36%). These 18 infants included 10 (43%) out of 23 of birthweight less than or equal to 1500 g, and 3 (27%) out of 11 of birthweight 1501-2000 g. An unexpected feature was the recognition of intraventricular haemorrhage in 5 of the 13 infants greater than 2000 g birthweight. On sequential daily scans intraventricular haemorrhage was diagnosed most often in the first 2 days of life and abnormal ventricular echoes persisted for up to 12 days thereafter. Late development of hydrocephalus was recorded in 2 infants. Real-time ultrasound provides the neonatologist with a practical method for diagnosis and monitoring of intracranial lesions in the ill neonate and is a valuable, non-invasive, and safe tool for studying the pathophysiology of neurological handicap in infancy.
Full text
PDF
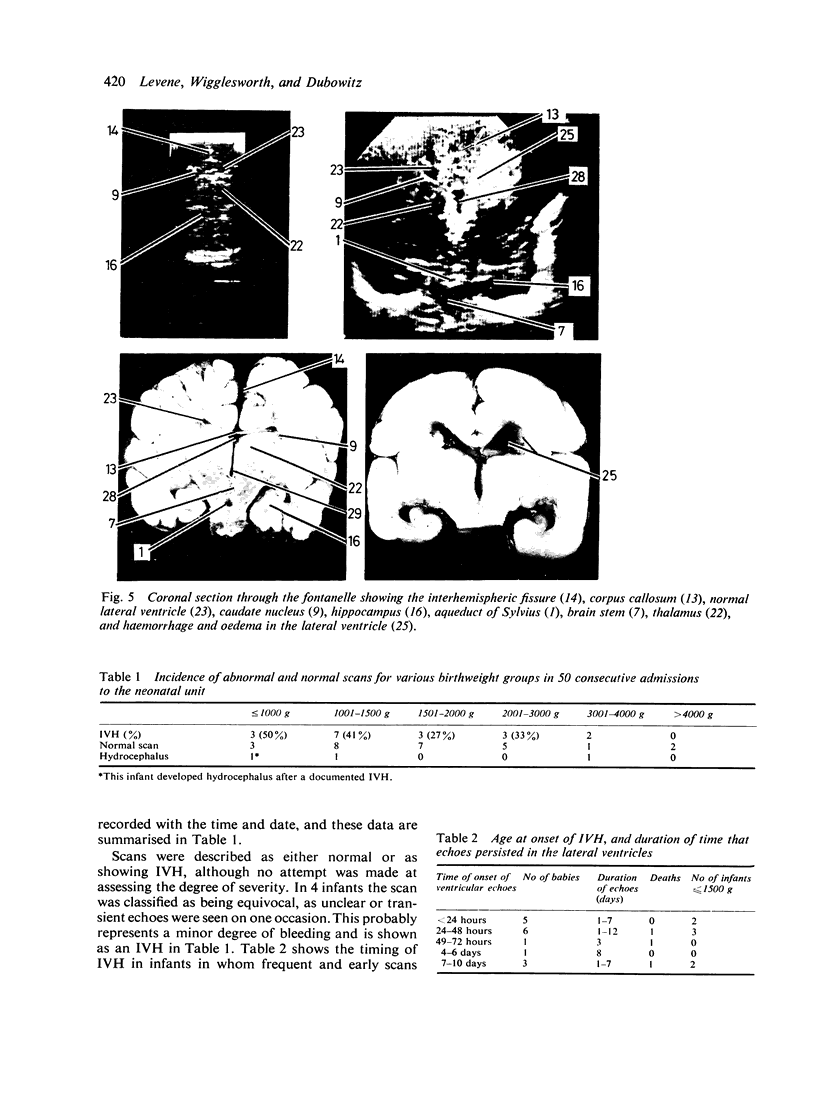
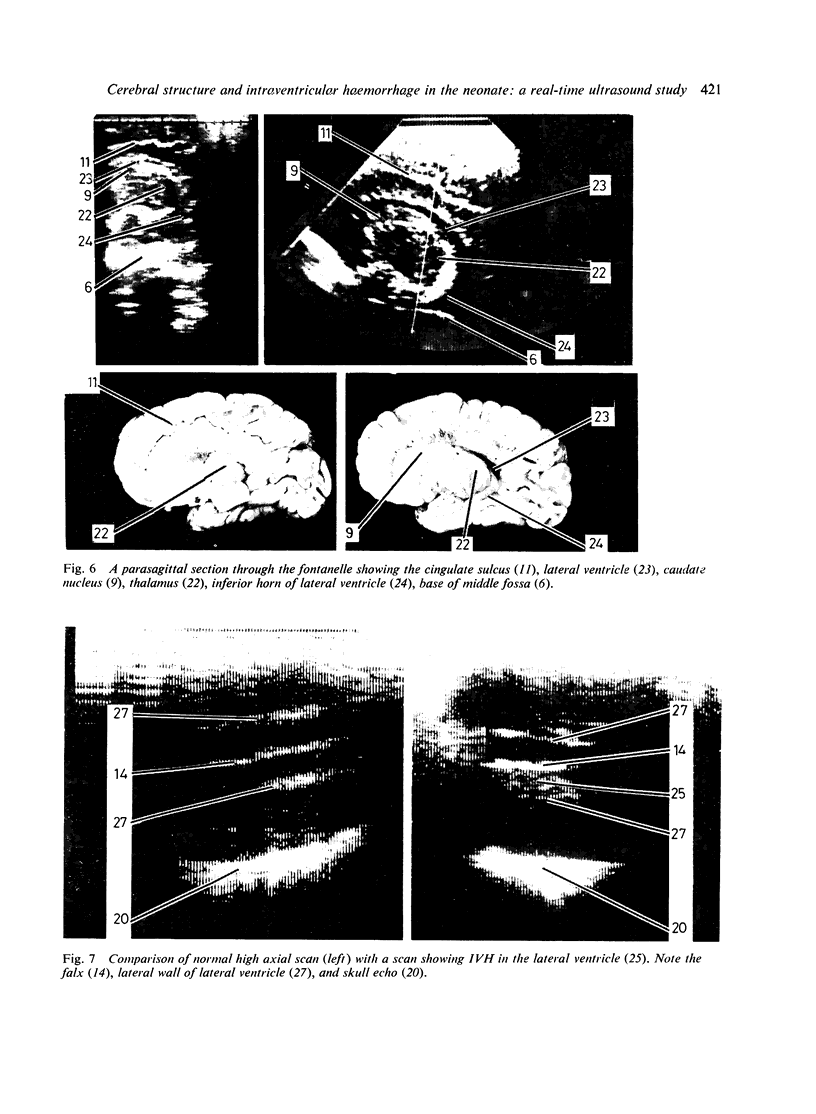



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bejar R., Curbelo V., Coen R. W., Leopold G., James H., Gluck L. Diagnosis and follow-up of intraventricular and intracerebral hemorrhages by ultrasound studies of infant's brain through the fontanelles and sutures. Pediatrics. 1980 Nov;66(5):661–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein J., Papile L. A., Burstein R. Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in premature newborns: a prospective study with CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Apr;132(4):631–635. doi: 10.2214/ajr.132.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright G. W., Culbertson K., Schreiner R. L., Garg B. P. Changes in clinical presentation of term infants with intracranial hemorrhage. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1979 Dec;21(6):730–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1979.tb01694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole V. A., Durbin G. M., Olaffson A., Reynolds E. O., Rivers R. P., Smith J. F. Pathogenesis of intraventricular haemorrhage in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Sep;49(9):722–728. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.9.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. W. Ultrasound examination of neonatal heads. Lancet. 1979 Jul 7;2(8132):38–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Palmer P., Verghote M. A new approach to the neurological assessment of the preterm and full-term newborn infant. Brain Dev. 1980;2(1):3–14. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(80)80003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson P., Fujimura M., Howat P., Howes D., Keeling J., Robinson R. O., Salisbury D., Tizard J. P. Timing of intraventricular haemorrhage. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Mar;52(3):183–187. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.3.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton G., Wigglesworth J. S. Origin of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm infant. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Sep;51(9):651–659. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.9.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthy K. S., Shannon D. C., DeLong G. R., Todres I. D., Davis K. R. Neurologic sequelae in the survivors of neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Pediatrics. 1979 Aug;64(2):233–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEKSELL L. Echo-encephalography. I. Detection of intracranial complications following head injury. Acta Chir Scand. 1956 Feb 16;110(4):301–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larroche J. C. Post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus in infancy. Anatomical study. Biol Neonate. 1972;20(3):287–299. doi: 10.1159/000240472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech R. W., Kohnen P. Subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhages in the newborn. Am J Pathol. 1974 Dec;77(3):465–475. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees R. F., Harrison R. B., Sims T. L. Gray scale ultrasonography in the evaluation of hydrocephalus and associated abnormalities in infants. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Apr;132(4):376–378. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120290048008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma P. A., Miner M. E., Morriss F. H., Jr, Adcock E. W., 3rd, Denson S. E. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the neonate born at term. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Sep;133(9):941–944. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130090069013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape K. E., Blackwell R. J., Cusick G., Sherwood A., Houang M. T., Thorburn R. J., Reynolds E. O. Ultrasound detection of brain damage in preterm infants. Lancet. 1979 Jun 16;1(8129):1261–1264. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds E. O., Taghizadeh A. Improved prognosis of infants mechanically ventilated for hyaline membrane disease. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jul;49(7):505–515. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.7.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. L., Rosenbaum A. E., Matzuk T., Guthkelch A. N., Heinz E. R. Detection of dilated cerebral ventricles in infants: a correlative study between ultrasound and computed tomography. Radiology. 1979 May;131(2):447–451. doi: 10.1148/131.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiantos A., Victorin L., Relier J. P., Dyer N., Sundell H., Brill A. B., Stahlman M. Intracranial hemorrhage in the prematurely born infant. Timing of clots and evaluation of clinical signs and symptoms. J Pediatr. 1974 Dec;85(6):854–859. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80360-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Neonatal intracranial hemorrhage. Pathophysiology, neuropathology, and clinical features. Clin Perinatol. 1977 Mar;4(1):77–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigglesworth J. S., Keith I. H., Girling D. J., Slade S. A. Hyaline membrane disease, alkali, and intraventricular haemorrhage. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Oct;51(10):755–762. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.10.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigglesworth J. S., Pape K. E. An integrated model for haemorrhagic and ischaemic lesions in the newborn brain. Early Hum Dev. 1978 Jul;2(2):179–199. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(78)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]