Fig. (1).
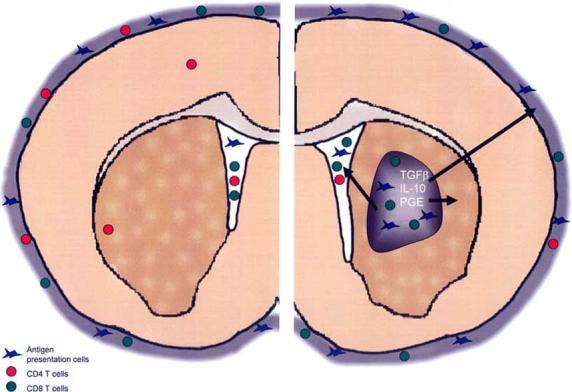
Immune cell surveillance of the normal and tumor bearing brain. In the normal brain, only memory CD4+ T-cells are found within the brain parenchyma while other immune cell types are restricted to the cerebrospinal fluid and meningeal layers. Tumors affect the local and systemic immune environment to evade immune detection by producing cytokines like TGFβ, IL-10 and PGE. CD4+ T-cell numbers are reduced systemically. Meanwhile tumors are infiltrated with macrophages and CD8+ T-cells whose normal immunological functions are blocked in the tumor environment.
