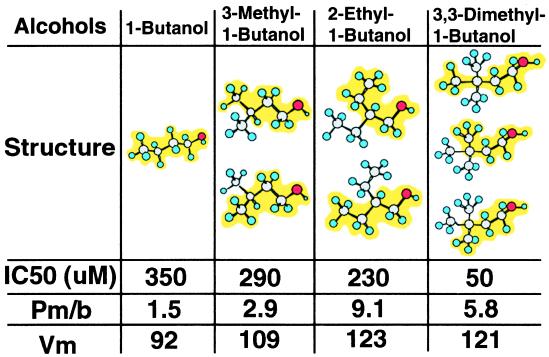
Figure 2.
Relation between the number of 1-butanol moieties and the potency for alcohol inhibition of cell–cell adhesion. Dose–response curves for the mean percent inhibition of cell–cell adhesion in BMP-7-treated NG108–15 cells were calculated from three to six independent experiments. The IC50 was determined by log-logit analysis of the mean data (not shown). The number of alignments that can present a 1-butanol moiety (highlighted in yellow) to a target are depicted for each alcohol. Also shown is the membrane/buffer partition coefficient (Pm/b) and molar volume (Vm) of each alcohol. Note that 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol, which can present a 1-butanol moiety from three possible alignments, is less lipid soluble than 2-ethyl-1-butanol, but more than 4 times as potent.