Figure 4.
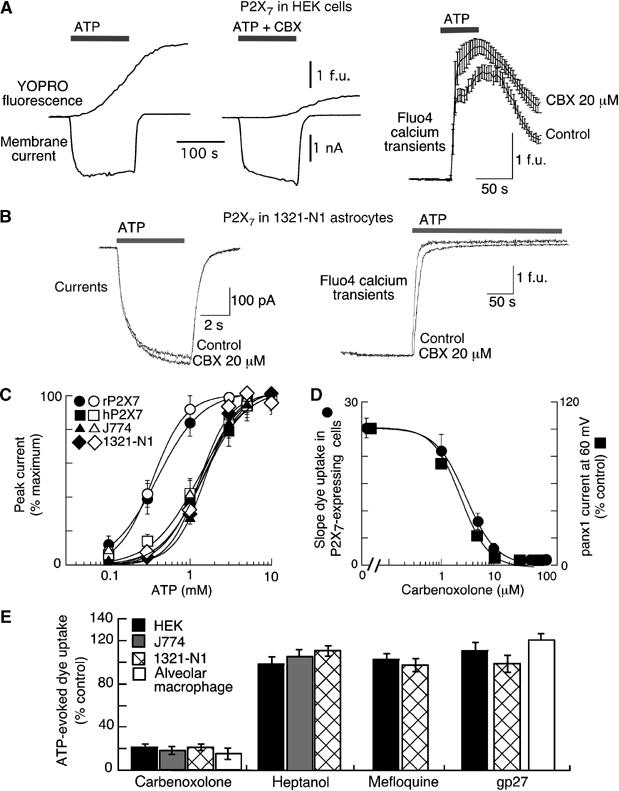
CBX but not other connexin channel blockers blocks ATP-mediated dye-uptake without inhibiting P2X7R activation. (A, B) Membrane currents, YOPRO-1 uptake and Fluo4 calcium transients (as indicated) recorded from HEK (A) or 1321-N1 (B) cells expressing P2X7Rs. CBX (20 μM) effectively blocked YOPRO-1 uptake without altering currents or calcium transients. All recordings obtained from physically isolated, single cells. (C) ATP concentration–response curves for membrane current (recorded at −60 mV holding potential) from all experiments as illustrated in (A) and (B), in control (closed symbols) and in 20 μM CBX (open symbols) for HEK cells expressing rat or human P2X7R, for 1321-N1 cells expressing human P2X7R and for mouse J774 macrophage, as indicated. CBX had no effect. (D) Concentration–response curve for CBX inhibition of dye uptake (circles) in P2X7R-expressing cells and for inhibition of panx1 currents recorded from HEK cells (squares) transfected with panx1 expression vector. (E) Summary of actions of several nonspecific connexin channel blockers to inhibit P2X7R-induced dye uptake from cells ectopically (HEK and 1321-N1) or endogenously (mouse J774 and human alveolar macrophage) expressing P2X7R. Concentrations used were CBX (20 μM), heptanol (200 μM), mefloquine (100 μM) and gp27 (1 mM); each value is mean±s.e.m. from 4 to 12 experiments.
